Deep learning _ loss function (MSE, MAE, Smoothl1_loss ...)
tags: Pytorch assault Machine learning Depth study artificial intelligence algorithm python
@TOC
Summarize the advantages and disadvantages of comparison of MSE loss functions, MAE loss functions, and smooth l1_loss loss functions
1, common MSE, MAE loss function
1.1, mean square error MSE
Mean Square Error, MSEIt is the most common error in the returns loss function, which is between the predicted value f (x) and the target value y.Difference square and meanThe formula is as follows:

The picture belowMean square errorThe curve distribution of the value, where the minimum value is the position of the predicted value is the target value. We can see more rapidly increases with the increase in the loss of the error.
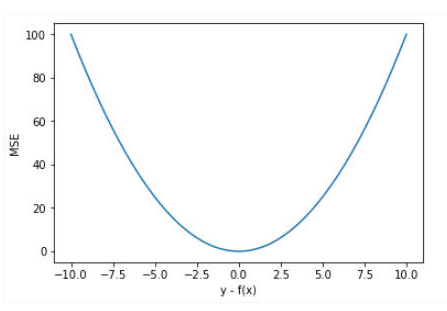
- advantage: MSE's function curve is smooth, continuous, and can be guided to facilitate the use of gradient drop algorithms, which is a commonly used loss function. Moreover, as the error decreases, the gradient is also reduced, which facilitates convergence, even if the fixed learning rate is used, can also converge to the minimum.
- Disadvantage: When the difference between the real value Y and the predicted value f (x) is greater than 1, the error is enlarged; and when the difference is less than 1, the error is reduced, which is determined by the square. MSE gives a larger error (> 1) to give a smaller penalty (<1). That is to say,Sensitive to the group points, affected by it。
If there is an off group point in the sample, MSE will give a higher weight of the group point, which sacrifices the prediction effect of other normal point data, and ultimately reducing the overall model performance. As shown below:
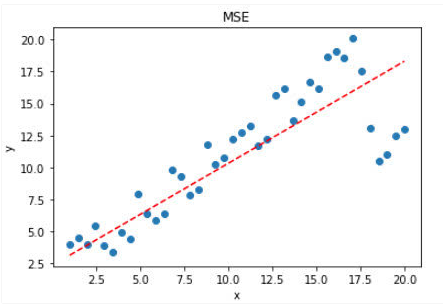
visible,Using the MSE loss function, the influence of the group is large, although only 5 out of the sample, butFitted straight lineStill comparisonBe biased。
1.2, average absolute error MAE
Average absolute error (MAE)Is another common regression loss function, it is the target value and the predicted valueWestern absolute value and meanRepresented the average error amplitude of the predicted value, without the need to consider the direction of the error (Note:Average deviation error MBEIt is the error in the direction considering, the residual and the range is 0 to ∞, the formula is as follows:

- advantage: There is an advantage of MAE compared to MSE, which is not so sensitive to the group points. Because MAE calculates an absolute value of the error (Y-F (x)), the penalty is fixed for any size difference. Regardless of what kind of input values, there is a stable gradient, which does not cause gradient explosion problems, which have a relatively robust solution.
- Disadvantage: The MAE curve is continuous, but is not guided at (Y-F (x) = 0). Moreover, MAE is equally equal, which means that even for small loss values, its gradient is also large. This is not conducive to the convergence and model of the function.
The effect of MAE is better than the MSE for data on the outstanding data on the above.
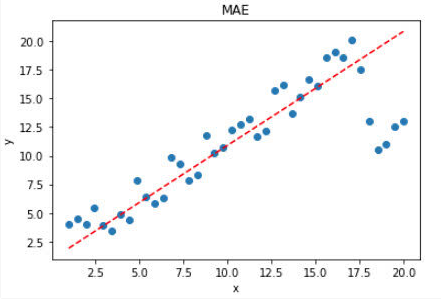
Obviously, using the MAE loss function, the impact of the group points is small, and the fitted straight line can better characterize the distribution of normal data.
1.3, MSE and MAE selection
- FromSolution of gradientas well asconvergenceon,MSE is better than MAE. MSE can be guided everywhere, and the gradient value is also dynamically changed, and it is possible to quickly converge; and MAE is not guided at 0 points, and its gradient remains unchanged. For a small loss value, its gradient is also very large. In deep learning, it is necessary to use changes to the rate of learning, and the learning rate is reduced when the loss value is small.
- CorrectUnion (abnormal) valueSo processing,MAE should be obvious than MSE。
If the off group (anomaly value) needs to be detected, you can select MSE as a loss function; if the outbound point is only treated as a damaged data, MAE can be selected as the loss function.
In shortMAE is more stable as the loss function and is not sensitive to the outgamous value, but its derivative is discontinuous, and the efficiency is low. In addition, in deep learning, the convergence is slow. The MSE derivative is highly solved, but it is sensitive to the outgamous value, but the derived derivative of the extent can be used to avoid this.
Under certain circumstancesThe above two loss functions cannot meet the needs. For example, if the target value of 90% of the sample in the data is 150, 10% is left between 0 and 30. Then the model using MAE as a loss function may ignore 10% of the abnormal point, and the predicted value of all samples is 150. This is because the model is predicted in meditile. The model using MSE will give a lot of predicted values between 0 and 30 because the model is offset to an abnormal point.
In this situationBoth MSE and MAE are unsuitable, simple ways to transform target variables, or use other loss functions, such as huber, log-cosh, and positioner loss.
2, L1_LOSS and L2_LOSS
2.1, l1_loss and l2_loss
- L1 norm loss functionAlso known as the minimum absolute deviation (LAD), minimum absolute value error (LAE). In general, it is the target value y and the estimated value F (xi)The sum of absolute differencesminimize:

- L2 norm loss functionAlso known as the minimum square error (LSE). In general, it is the target value Y and the estimated value F (xi)Square and S of the differenceminimize:

L1 norm and L2 norm as a loss functionthe differenceSummarized as follows:

to sum upIn fact, we found that the so-called L1_LOSS and L2_LOSS and the previous MAE, the MSE loss function is only a difference between 1 / n, so their advantages and disadvantages are interoperability.
2.2, several key concepts
- Robustness
Because the robustness of the minimum absolute deviation method is better than the minimum square, it has applications in many occasions. The minimum absolute deviation is robust because it can process an exception value in the data. This may be useful in research that may be safely and effectively ignored in those abnormal values. If you need to consider any or all of the exception values, the minimum square error is better.
In an intuitive say, because the L2 norm will be equredient in square (if the error is greater than 1, the error will be large), the error of the model is larger than the L1 norm, so the model will be more sensitive to this sample, this requires adjustment Model to minimize errors. If this sample is an exception value, the model needs to be adjusted to accommodate a single exception value, which sacrifices many other normal samples, because the error of these normal samples is smaller than the single error value. - stability
The instability of the minimum absolute deviation method means that the return line may jump very much for a small horizontal direction of the data set. On some data structures, this method has many consecutive solutions; however, a minimal movement of the data set will skip a number of continuous solutions of a data structure in a certain area. (The Method Has ContiGuars; However, by Moving a Datum A Small Amount, One Could "Jump Past" A Configuration Which Has Multiple Solutions That SPAN A Region.) After skipping this area, the minimum Absolute deviation line may be more tilted than the previous line. Conversely, the solve the descending method is stable because the return line always moves only slightly for any minute fluctuation of a data point;,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
3. SMOoth L1 loss function (also known as Huber loss function)
The loss functions used in the FASTER R-CNN and the return of the border are SMOOTH (L_1) as a loss function. In fact, as the name suggests, SMOoth L1 is said to L1 after the smooth, said that the shortcomings of L1 losses is that there is a discount, not smooth, how do you make it smooth?
SMOOTH L1 loss functionfor:

among them,

Smooth L1 can limit gradient from two aspects:
- When the prediction box is too large, the gradient value is not too large when the Ground Truth is too large.
- When the prediction frame is different from GROUND TRUTH, the gradient value is sufficiently small.
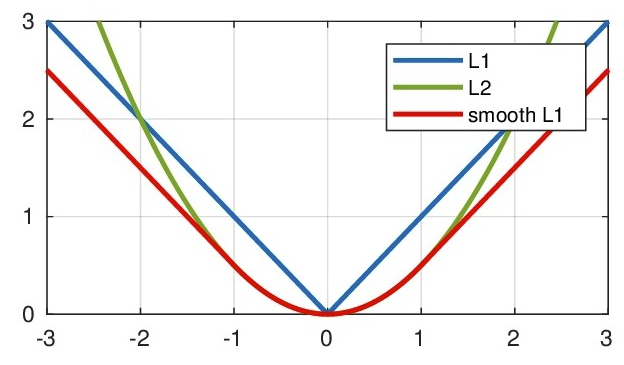
As can be seen from the above, the function is actually a segment function, actually between [-1, 1], which is l2 loss, which solves the loss of L1, outside the [-1, 1] interval, In fact, L1 losses, which solves the problem of outbound gradient explosion.
Pytorch implementation 1
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='mean')
Pytorch implementation 2
def _smooth_l1_loss(input, target, reduction='none'):
# type: (Tensor, Tensor) -> Tensor
t = torch.abs(input - target)
ret = torch.where(t < 1, 0.5 * t ** 2, t - 0.5)
if reduction != 'none':
ret = torch.mean(ret) if reduction == 'mean' else torch.sum(ret)
return ret
You can also add a parameter BETA to control, what range of errors use MSE, what is the error used by MAE.
Pytorch implementation 3
def smooth_l1_loss(input, target, beta=1. / 9, reduction = 'none'):
"""
very similar to the smooth_l1_loss from pytorch, but with
the extra beta parameter
"""
n = torch.abs(input - target)
cond = n < beta
ret = torch.where(cond, 0.5 * n ** 2 / beta, n - 0.5 * beta)
if reduction != 'none':
ret = torch.mean(ret) if reduction == 'mean' else torch.sum(ret)
return ret
4, summary
For most CNN networks, we generally use L2-Loss instead of L1-Loss because L2-LOSS convergence speed is much faster than L1-LOSS.
For border prediction regression, the square loss function (L2 loss) can also be selected, but the disadvantage of the L2 norm is that when there is an outlier, these points will account for the main components of LOSS. For example, the true value is 1, predicted 10 times, there is a forecast value of 1000, the remaining predicted value is about 1, obviously the Loss value is mainly determined by 1000. Therefore, FASTRCNN uses a slightly slower absolute loss function (SMOoth L1 loss), which is growing as the error is raised, not the square growth.
The difference between the SMOoth L1 and L1 Loss functions is that the derivative of L1 LOSS is not unique at 0 points, which may affect convergence. SMOoth L1 solution is to use a square function near 0 points to make it smoother.
Advantages of SMOoth L1
- Compared to the L1 loss function, it can converge faster;
- Compared to the L2 loss function, the abnormal value is not sensitive to the off group, the gradient change is relatively smaller, and the training is not easy to run.
Intelligent Recommendation
[Deep Learning Basics] Manually implementing a multi -layer perception MLP neural network (spread forward, RELU activation function, MSE loss function)
Manually realized the forward and backward transmission of a full connection neural network with 10 hidden layers (mainly completing school homework ... tat) Handwriting the RELU activation function a...
Some simple summary on depth learning loss function MSE
MSELOSS loss function Chinese name is: mean square loss function, the formula is as follows: (xi-yi) square The dimensions of Loss, X, Y here are the same, which may be a vector or matrix, i is a subs...
Deep learning - loss function (loss)
All learning algorithms in deep learning must have a function that minimizes or maximizes, called a loss function, or "objective function" or "cost function". The loss function is ...
Loss function (MSE and cross entropy)
Fully connected layer solves MNIST: Only one fully connected layer solves the MNIST dataset Neural Network Propagation: Explained the weight update process This series of articles is to summarize the ...
More Recommendation
BCE, CE, MSE loss function
1. Bceloss The code implementation provides two ways: one is to call the official NN.Bceloss API, and the other is the custom function implementation: 2. Celoss The calculation process of the CE descr...
Deep learning - loss function
Deep learning - loss function Before due to personal laziness made a very poor piece of paper, now correct the error, send a note is learning tensorflow In the process of constructing the neural netwo...
Loss function of deep learning
1.tf.nn.l2_loss tf.nn.l2_loss(t, name=None) L2 Loss.Computes halfthe L2 normofa tensorwithoutthesqrt: The function of this function is to use the L2 norm to calculate the error value of the tensor, bu...
Deep learning loss function
Classification problems and regression problems are two major categories of supervised learning. The commonly used loss function for classification problems is cross entropy tensorflow implementation ...
Deep learning-loss function
Loss function: In machine learning tasks, most supervised learning algorithms will have an objective function (Objective Function), and the algorithm optimizes the objective function, which is called ...