Transfer from: http://www.linkwan.com/gb/tech/htm/928.htm
1, the basics of Ping
The ping command believes that everyone is familiar with it, but there are not many people who can use the ping function to the maximum. Of course, I am not saying that I can let ping play the most functions. I only use the ping tool frequently. Also summarized some small experiences, and now share with you.
Ping is a term used by submarine personnel to indicate the response to the sonar pulse. Ping is a very useful TCP/IP tool in the network. Its main function is to detect network connectivity and analyze network speed.
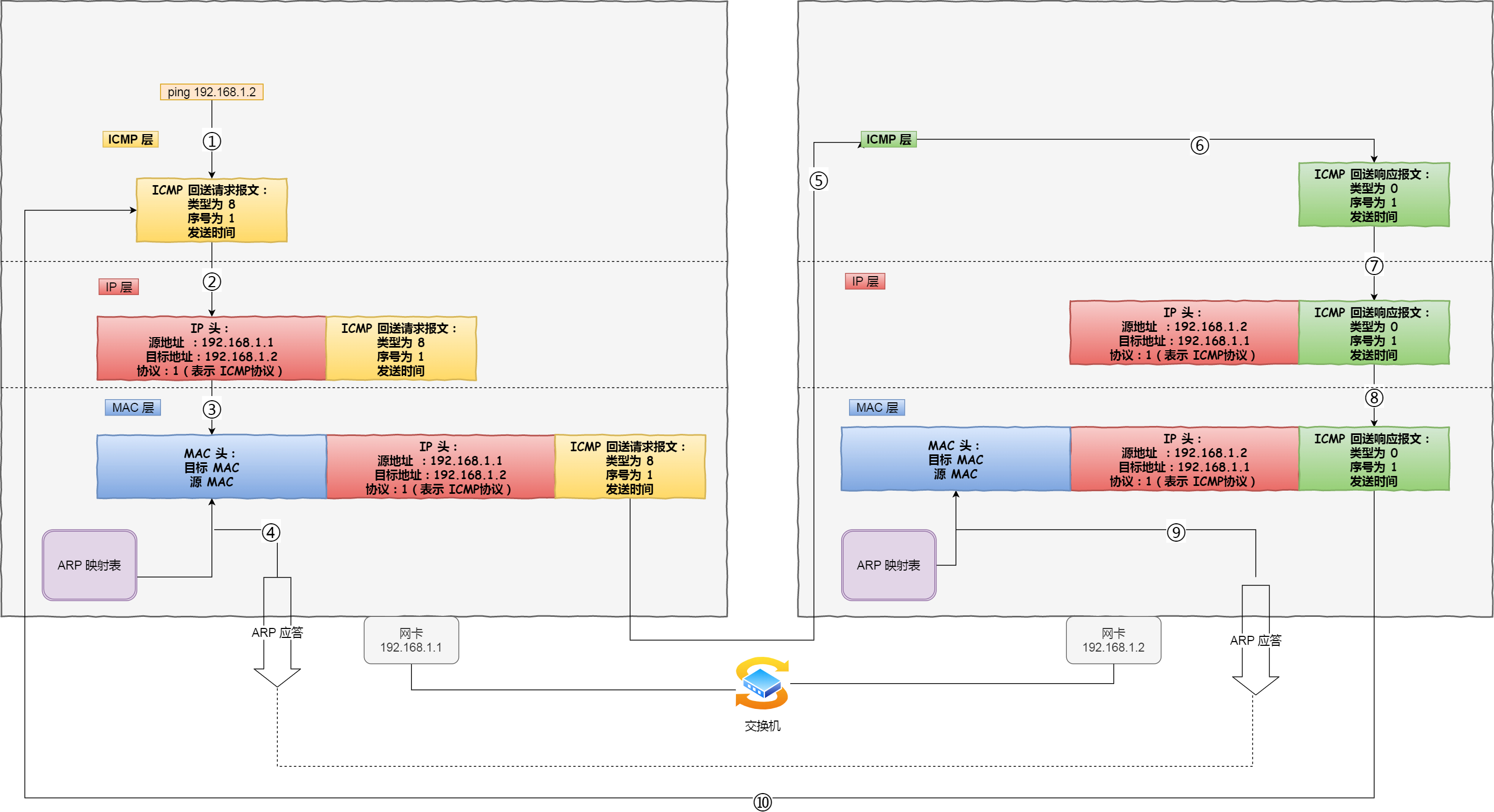
Ping has a good side and a bad side. Let me talk about the good side first. As mentioned above, the purpose of Ping is to detect the network together with the situation and analyze the network speed, but what is it used to display connectivity? This first needs to understand some parameters and return information of Ping.
2, Ping command detailed
First need to open the DOS command interface, by clicking the "Run" option in the start menu, enter "cmd", press Enter to open (as shown below).
After the carriage return
We enter ping /? Example ping The following are some parameters of PING (as shown):
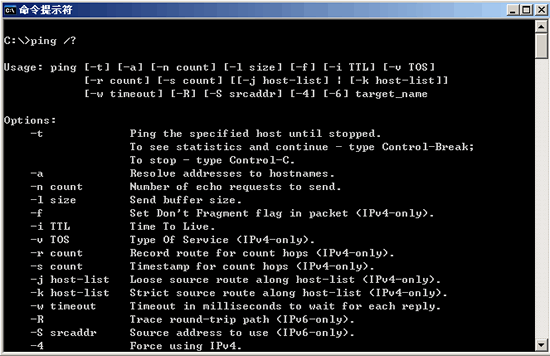
Let me explain to you, each parameter meaning and use.
ping [-t] [-a] [-n count] [-l length] [-f] [-i ttl] [-v tos] [-r count] [-s count] [-j computer-list] | [-k computer-list] [-w timeout] destination-list
-t Ping the specified computer until it is interrupted.
-a Resolves the address to a computer name.
-n count Send count The number of ECHO packets specified. The default is 4.
-l length Sends an ECHO packet containing the amount of data specified by length. The default is 32 bytes; the maximum is 65,527.
-f Send the "Do not segment" flag in the packet. Packets are not fragmented by the gateway on the route.
-i ttl Sets the Time to Live field to the value specified by ttl.
-v tos Sets the Service Type field to the value specified by tos.
-r count Records the routes of outgoing and returned packets in the Record Route field. Count can specify a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 9 computers.
-s count Specifies the timestamp of the number of hops specified by count.
-j computer-list Routes packets using the list of computers specified by computer-list. Continuous computers can be separated by intermediate gateways (route sparse sources). The maximum number of IPs allowed is 9.
-k computer-list Routes packets using the list of computers specified by computer-list. Continuous computers cannot be separated by intermediate gateways (routing strict sources) The maximum number of IPs allowed is 9.
-w timeout Specifies the timeout interval in milliseconds.
Destination-list Specifies the remote computer to ping.
3. How to use the Ping command to test network connectivity?
The connectivity problem is caused by many reasons, such as local configuration errors, remote host protocol failures, and of course, failures caused by devices.
First let's talk about the steps to use the Ping command.
There are five steps to checking connectivity using Ping:
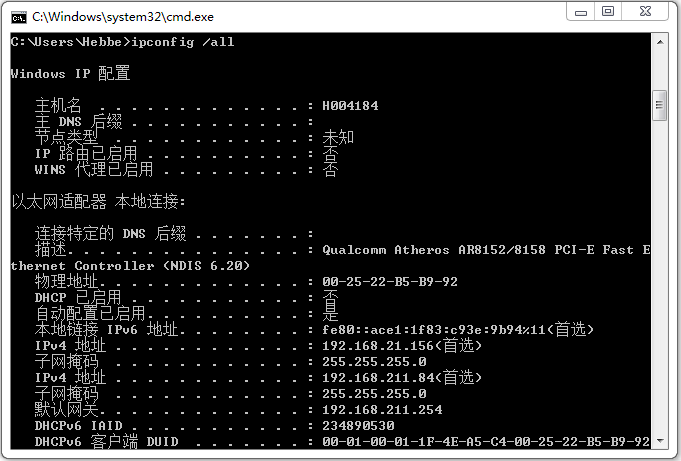
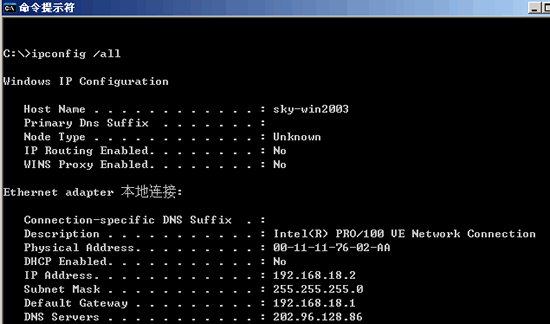
1. Use ipconfig /all to observe whether the local network settings are correct, as shown in the figure;
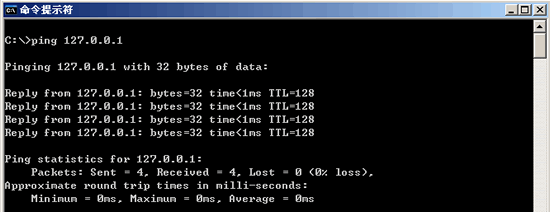
2. Ping 127.0.0.1, 127.0.0.1 The return address Ping return address is to check if the local TCP/IP protocol is set.
3. Ping the IP address of the machine, in order to check whether the IP address of the machine is set incorrectly;
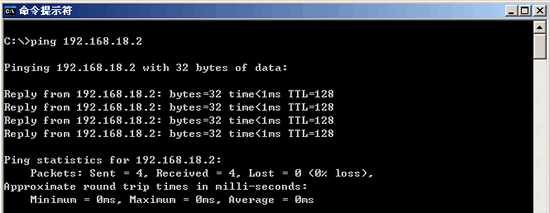
4. Ping the gateway of the local network or the IP address of the local network. This is to check whether the hardware device has a problem. You can also check whether the connection between the local network and the local network is normal. (This step can be ignored in non-LAN)
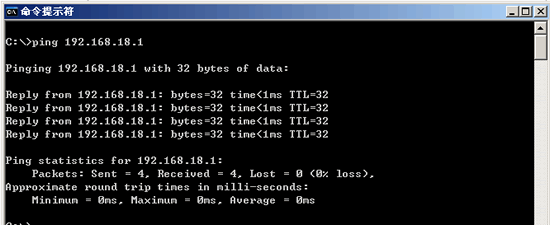
5. Ping the remote IP address. This is mainly to check whether the connection between the local network or the local device is normal.
4. How to use the Ping command to judge whether a link is good or bad?
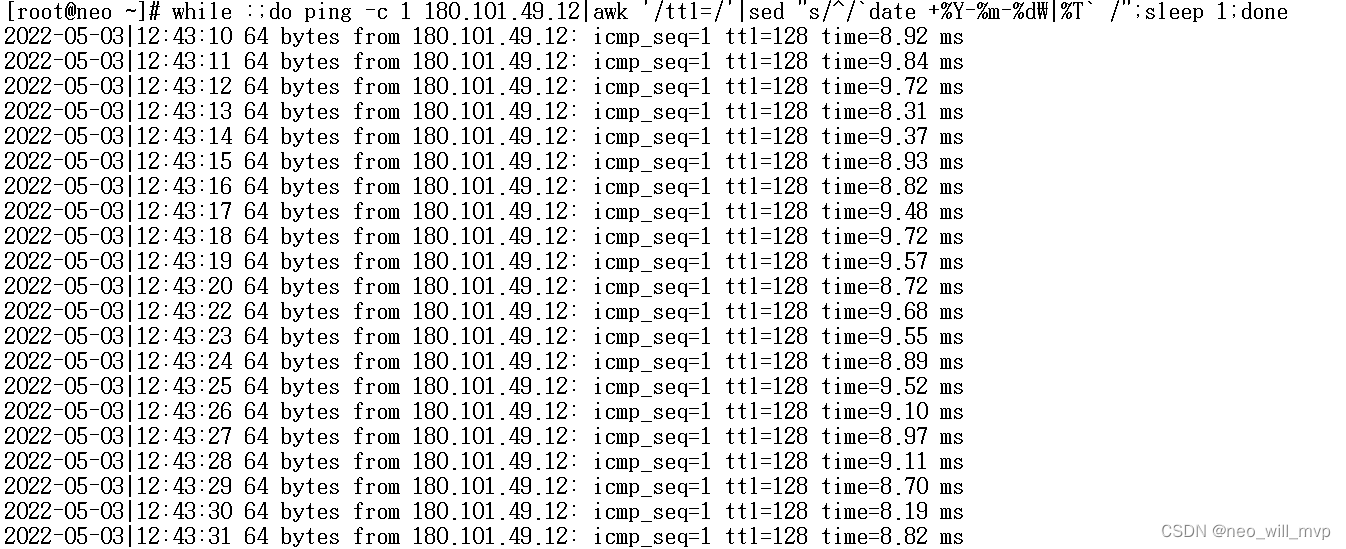
In addition to checking the connectivity of the network and detecting faults, the Ping command has an interesting use. It can use some of its return data to estimate how many bytes per second between you and a host.
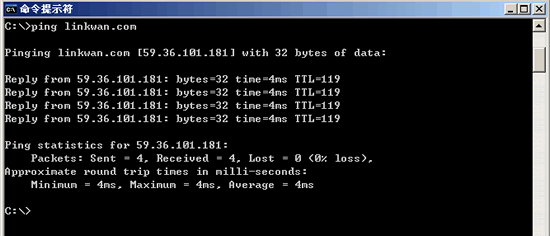
Let's first take a look at the data it has returned.

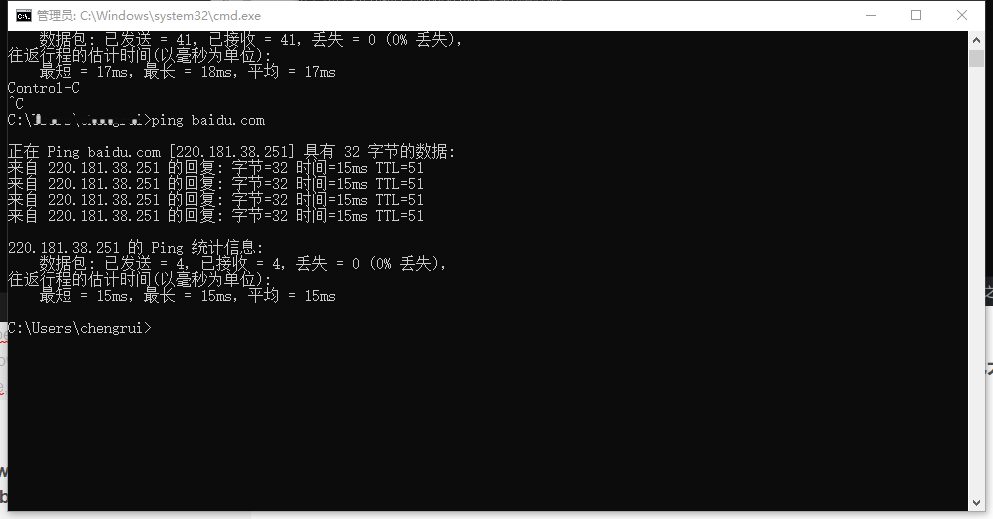
In the example "bytes=32" means that there are 32 bytes of test data in the ICMP message, and "time=4ms" is the round trip time. Sent sends multiple seconds packets, Received receives multiple response packets, Lost discards how many Minmum minimums, MAXimun maximums, Average averages. As shown in the figure, only 4MS time is used for back and forth. Lost =0 means that the number of lost packets is 0, and the network status is quite good. (For more details, use the -n parameter "ping –n 100 IP address" to ping 100 times. See the changes in Sent Received Lost Minmum MAXimun Average.)
5. Analysis of the information returned after Ping
1.Request timed out
This is the prompt message that everyone often encounters. Many articles say that this is the other machine to filter the ICMP data packet. From the above work process, this is not completely correct, at least there are several cases.
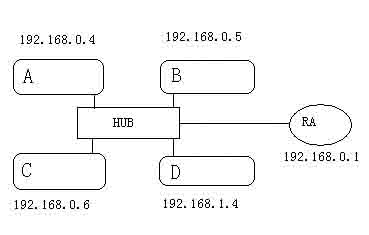
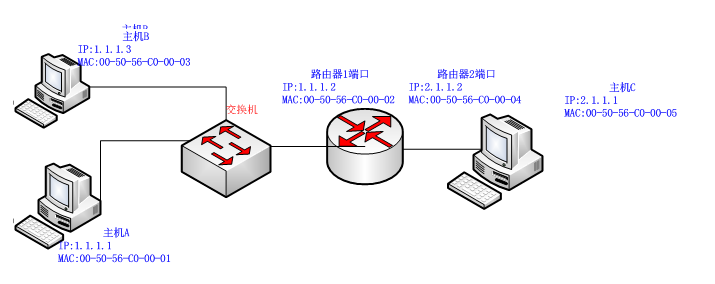
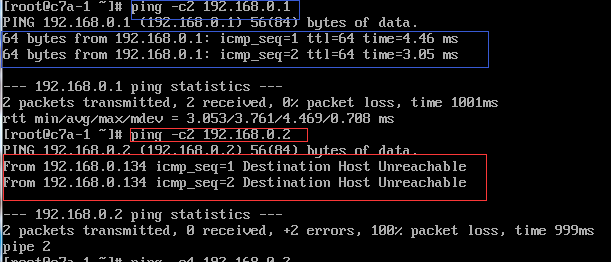
(1) The other party has been shut down, or there is no such address on the network: for example, PING 192.168.0.7 in host A in the above figure, or host B is turned off, PING 192.168.0.5 in host A will get timeout information.
(2) The other party is not in the same network segment as the user, and the other party cannot be found through the route. However, sometimes the other party does exist, and of course there is no information that returns the timeout.
(3) The other party does exist, but ICMP packet filtering (such as firewall settings) is set.
How do I know if the other party exists or does not exist? You can use the Ping command with the parameter -a to detect the other party. If you can get the NETBIOS name of the other party, it means that the other party exists. There is a firewall setting. If it is not available, most of them are The other party does not exist or shut down, or is not in the same network segment.
(4) Error setting IP address
Under normal circumstances, a host should have a network card, an IP address, or multiple network cards, multiple IP addresses (these addresses must be on different IP subnets). But if the TCP/IP setting of a computer's "dial-up network adapter" (equivalent to a soft network card) is set to an IP address on the same subnet as the network card IP address, this way, in the view of the IP layer protocol, this The host has two different interfaces in the same network segment. When pinging other machines from this host, there is such a problem:
A. The host does not know which network interface to send the packet to because there are two network interfaces connected to the same network segment.
B. The host does not know which address to use as the source address of the packet. Therefore, from this host to ping other machines, the IP layer protocol will not be able to process. After the timeout, Ping will give a "Timeout No Answer" error message. However, when pinging this host from other hosts, the request packet is from a specific network card. ICMP only needs to simply swap the destination and source address and change some flags. The ICMP response packet can be sent smoothly, and other hosts can also Successfully pinged this machine.
2.Destination host Unreachable
(1) The other party is not on the same network segment as itself, and they have not set the default route. For example, in the above example, the default route is not set in the A machine. When the Ping 192.168.0.1.4 is run, “Destination host Unreachable” will appear. .
(2) The network cable is faulty.
Here to explain the difference between "destination host unreachable" and "time out", if the route table of the passing router has a route to the destination, and the target is unreachable for other reasons, then "time out" will appear, if If there is no route to the destination in the routing table, then "destination host unreachable" will appear. 3.Bad IP address
This message indicates that you may not be connected to the DNS server, so the IP address cannot be resolved, or the IP address does not exist.
4.Source quench received
This information is special and it has a low probability of appearing. It means that the other party or the server in the middle is too busy to respond.
5.Unknown host - unknown host
This error message means that the name of the remote host cannot be converted to an IP address by the Domain Name Server (DNS). The cause of the failure may be that the domain name server is faulty, or its name is incorrect, or the communication line between the network administrator's system and the remote host is faulty.
6.No answer - no response
This failure indicates that the local system has a route to the central host but does not receive any information it sends to the central host. The cause of the failure may be one of the following: the central host is not working; the local or central host network configuration is incorrect; the local or central router is not working; the communication line is faulty; the central host has routing problems.
7.Ping 127.0.0.1:127.0.0.1 is the local loop address
If the address cannot be pinged, the local machine TCP/IP protocol does not work properly.
8.no rout to host: The NIC is not working properly.
9.transmit failed, error code: 10043 NIC driver is not working properly.
10.unknown host name: The DNS configuration is incorrect.
The above is some of the experience and skills that I have summarized in the process of “Ping”. I hope that I can help you with your work and study.