Data algorithm and structure-merge sort, binary search
1. Merge Sort
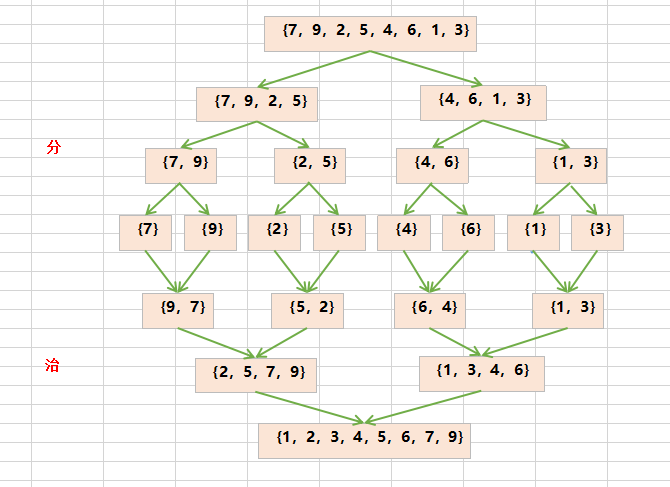
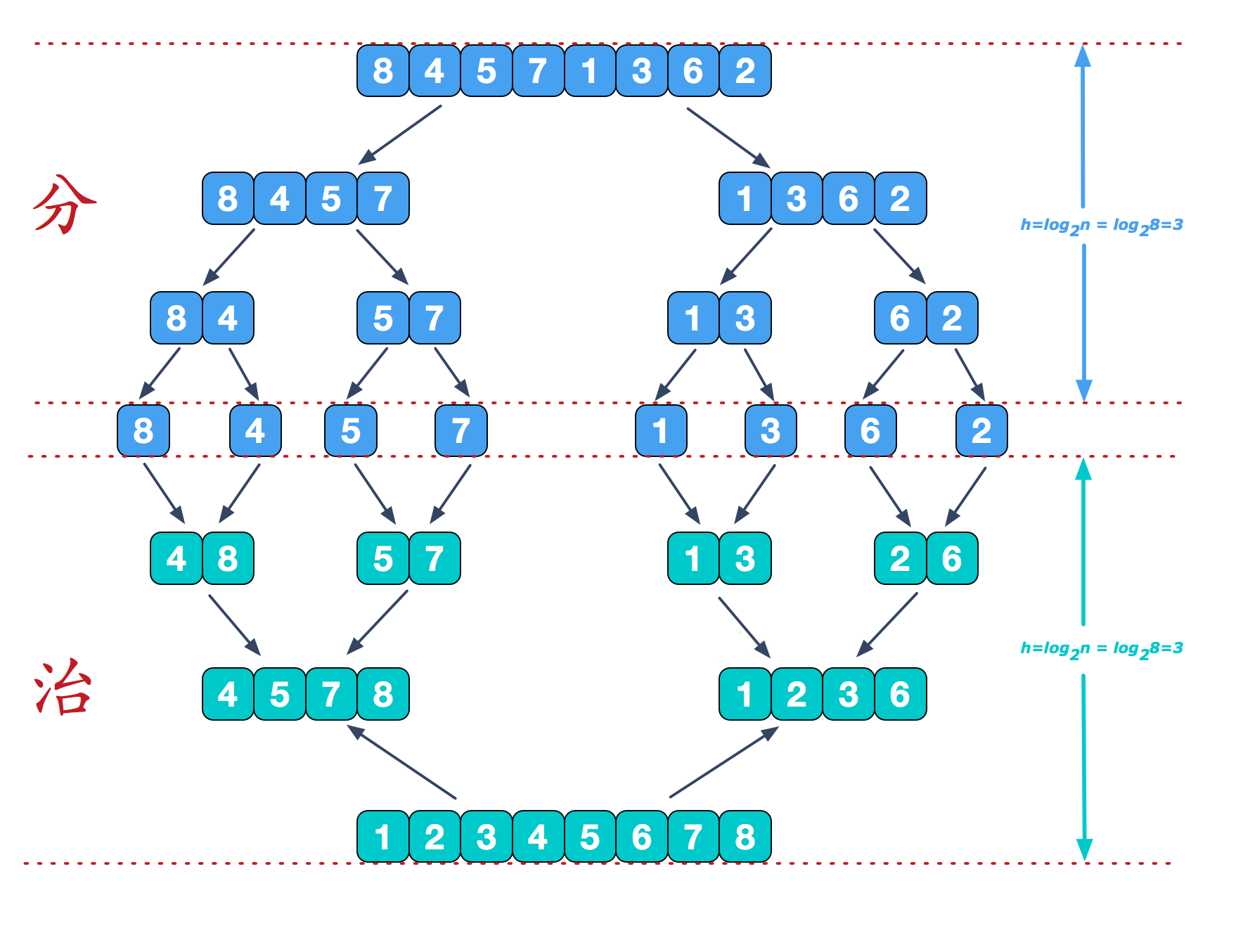
Merge sort is a very typical application of divide and conquer. The idea of merge sort is to decompose the array recursively first, and then merge the array.
After decomposing the array to the smallest value, then merge the two ordered arrays. The basic idea is to compare the first number of the two arrays. Move one back. Then compare until one array is empty, and finally copy the remaining part of the other array.
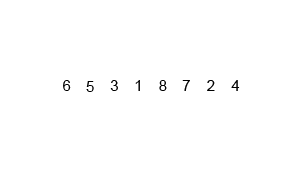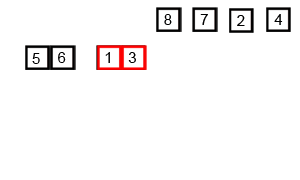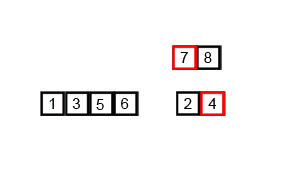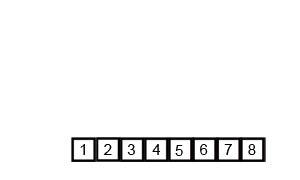
1.1 Implementation of merge sort
def merge_sort(alist):
if len(alist) <= 1:
return alist
# Binary decomposition
num = len(alist)/2
left = merge_sort(alist[:num])
right = merge_sort(alist[num:])
# Merge
return merge(left,right)
def merge(left, right):
'''Merge operation, merge the two ordered arrays left[] and right[] into one big ordered array'''
#left and right index pointer
l, r = 0, 0
result = []
while l<len(left) and r<len(right):
if left[l] < right[r]:
result.append(left[l])
l += 1
else:
result.append(right[r])
r += 1
result += left[l:]
result += right[r:]
return result
1.2 Time complexity of merge sort
Optimal time complexity: O(nlogn)
Worst time complexity: O(nlogn)
Stability: stable
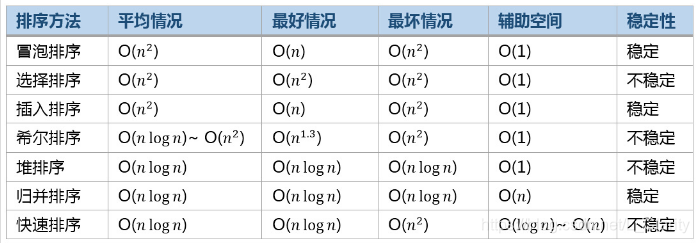
2. Comparison of the efficiency of common sorting algorithms
3. Search
Searching is the algorithmic process of finding a specific item in a collection of items. Search usually answer is true or false because of whether the item exists. Several common methods of searching: sequential search, binary search, binary tree search, hash search.
3.1 Binary search
Binary search
Advantages: fewer comparisons, fast search speed, good average performance
Disadvantages: The table to be checked is required to be an ordered table, and it is difficult to insert and delete.
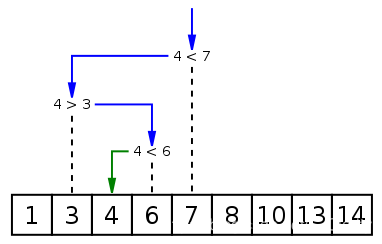
3.1.1 The realization of binary search
① Non-recursive implementation
def binary_search(alist, item):
first = 0
last = len(alist)-1
while first<=last:
midpoint = (first + last)/2
if alist[midpoint] == item:
return True
elif item < alist[midpoint]:
last = midpoint-1
else:
first = midpoint+1
return False
testlist = [0, 1, 2, 8, 13, 17, 19, 32, 42,]
print(binary_search(testlist, 3))
print(binary_search(testlist, 13))
②Recursive realization
def binary_search(alist, item):
if len(alist) == 0:
return False
else:
midpoint = len(alist)//2
if alist[midpoint]==item:
return True
else:
if item<alist[midpoint]:
return binary_search(alist[:midpoint],item)
else:
return binary_search(alist[midpoint+1:],item)
testlist = [0, 1, 2, 8, 13, 17, 19, 32, 42,]
print(binary_search(testlist, 3))
print(binary_search(testlist, 13))
3.1.2 Time complexity of binary search
Optimal time complexity: O(1)
Worst time complexity: O(logn)
Intelligent Recommendation
Data structure and algorithm: Binary search tree/sort tree/search tree
The idea of pre-order traversal, middle-order traversal, and subsequent traversal of binary trees respectively introduces quick sort, tower of Hanoi, and merge sort. The addition, deletion, and chec...
Data Structure and Algorithm - Binary Search Tree (Binary Sort Tree) [19]
Linear tables are less efficient in addition and deletion, so we consider special trees, consider this storage structure, improve lookup efficiency, and dynamically add and delete efficiency. At this ...
【Data Structure and Algorithm】——Merge Sort
Original address:【Data Structure and Algorithm】——Merge Sort The merge sort (MERGE-SORT) is an effective sorting algorithm based on the merge operation. This algorithm is a very typical app...
Data structure-merge sort (algorithm)
basic introduction: Merger sorting (MERGE-SORT) is a sorting method that uses merged thought items. The algorithm uses the classic divide-and-conquer strategy (divide and divide the problem into some ...
Merge and sort of data structure and algorithm
I. Introduction Merge sorting is an effective sorting algorithm based on the merge operation. The algorithm usesDivide and conquer (Divide and Conquer)A very typical application. Second, algorithm thi...
More Recommendation
Data structure and algorithm (merge sort)
Merge sort Merge sort is a typical application of divide and conquer. The idea of merge sort is to recursively decompose the array first, and then merge the array. After decomposing the array to a m...
Data structure algorithm-merge sort
Let's start with recursion Time complexity formula of recursive function Merge sort Merge sort code Merge sort time complexity O(NlogN)O(NlogN)O(NlogN) Find the sum of the array Let's start with recur...
[Data structure and algorithm] merge sort
You can see the animation of merging and sorting in the MER tag of https://visualgo.net/zh/sorting. Merge sort: Time complexity: O(nlogn) Space complexity: O(n) Basic idea: Divide and conquer. 8 6 2 3...
Data structure merge sort algorithm
Merge sort algorithm:...
Data structure and algorithm-merge sort
Data structure and algorithm-merge sort Report an error 1. Stack overflow 2. Dynamic array 3. External symbols that cannot be resolved Code Report an error 1. Stack overflow 2. Dynamic array Prevent s...