Synchronous reset, asynchronous reset, asynchronous reset synchronous release
tags: MCU Single-chip microcomputer stm32 FPGA development
content
Advantages and disadvantages of synchronous reset:
Advantages and disadvantages of asynchronous reset:
3, asynchronous reset synchronous release
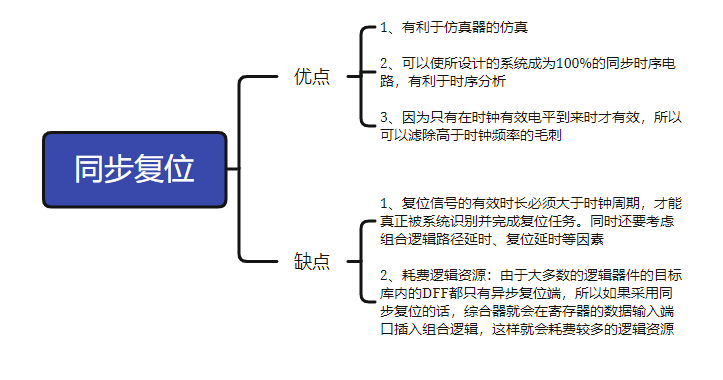
1, synchronous reset
Synchronous reset, that is, if the reset signal is valid, it can only reset the circuit on the clock rising edge.
always @ (posedge clk) begin
if (!rst_n)
xxxx;
end
Notice:In this always block, the sensitive amount is only one, that is, the rising edge of CLK, this meaning, only the Always block can be executed only in the rising edge of the CLK, otherwise it will not be executed. So if the reset signal is valid, it can only wait until the CLK rising edge can execute the ALWAYS block to reset the circuit!
Advantages and disadvantages of synchronous reset:
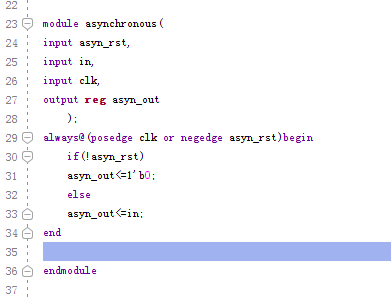
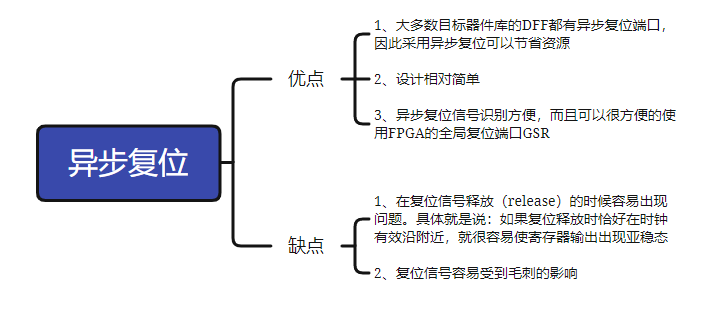
2, asynchronous reset
The reset signal is not controlled by the clock, regardless of whether the clock edge is coming, the system will reset the system as long as the reset signal is valid.
Generally, the reset signal is highly valid.
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
begin
if (!rst_n)
xxxx;
else if (xx)
begin
xxxx;
end
end
Notice:In this Always block, the sensitive amount is two, one is a posedge CLK, one is the falling edge of the reset signal RST_N (Negedge RST_N), and when the reset signal falls, what is the state of CLK, Execute the always block, ie, reset!
Advantages and disadvantages of asynchronous reset:
3, asynchronous reset synchronous release
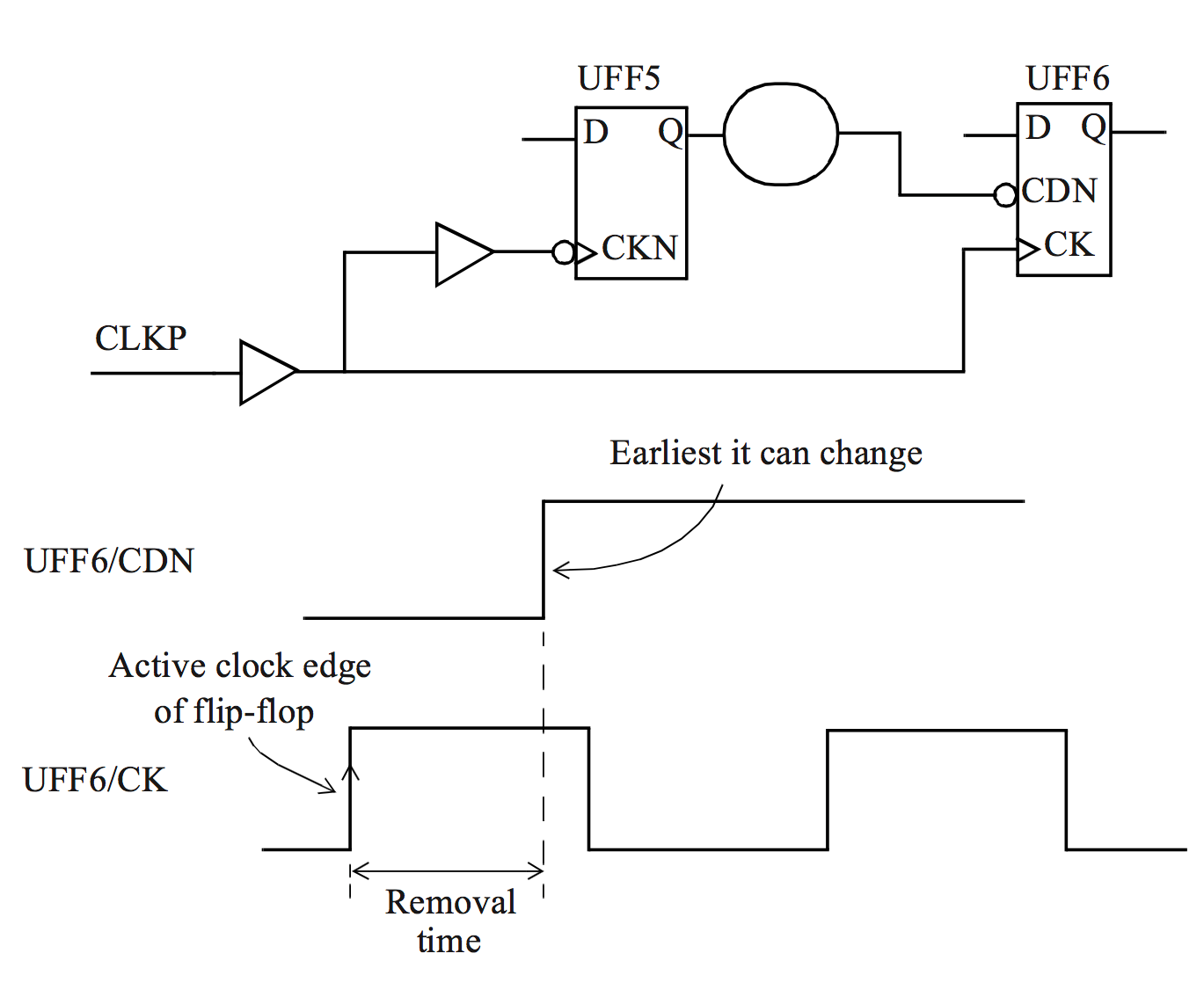
Suppose the reset signal is effectiverst_nWhen the reset signal is invalid, it is the release of the reset signal when the reset signal is pulled.
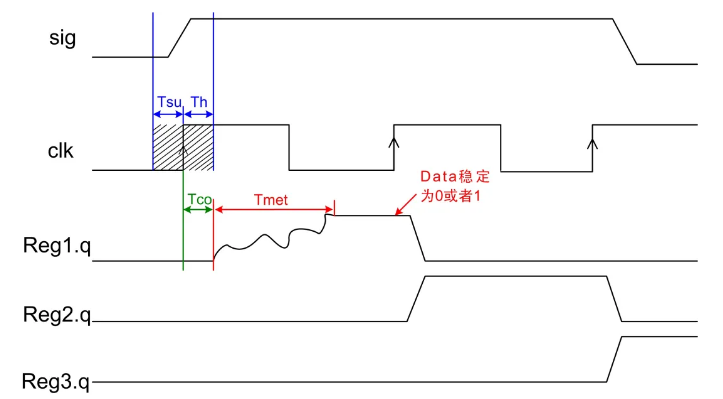
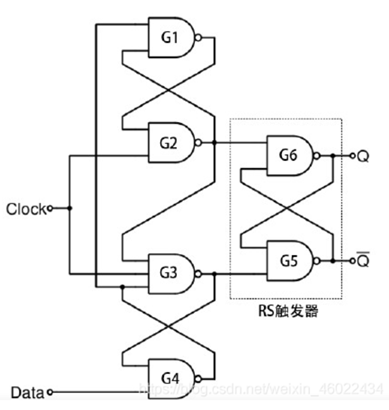
Since the asynchronous reset signal is unable to contact the clock, both are independent, so the release of the reset signal will have a certain probability that the circuit is metastable.
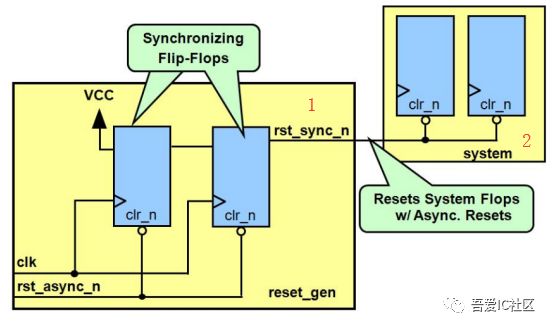
The so-called asynchronous reset synchronization is released at the RST_N signal, and the RST_N signal is released immediately, and in order to prevent the appearance of the aginet state, the RST_n signal is extended by the RST_n signal to reach a period of one cycle, reaching the clock. The purpose of the CLK edge synchronization.
The classic asynchronous reset synchronous release code is as follows:
module asyn_reset(
clk ,
rst_n ,
rst_s2
);
input clk ;
input rst_n ;
output reg rst_s2;
reg rst_s1;
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
rst_s1 <= 1'b0;
rst_s2 <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
rst_s1 <= 1'b1 ;
rst_s2 <= rst_s1 ;
end
end
endmodule
The integrated circuit is as follows:
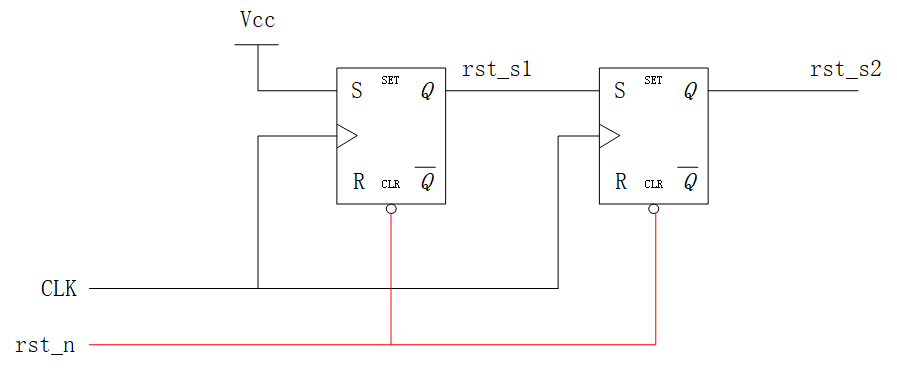
Reset signal is high, it is equivalent torst_nSampling high level;
Due to asynchronous reset needsClock rising edge is releasedTherefore, sorst_n=1After you let the signalrst_s1Level1Sampling, then play a shot of the registerrst_s2. Equivalent to high levels have been played two patchesrst_s2, Reaching the release of the reset signal and the clockclkThe purpose of synchronization.
references:
Understanding of "asynchronous reset, synchronous reset, asynchronous reset and synchronous release"
Intelligent Recommendation
Asynchronous reset and synchronous release in Verilog
There is a problem of metastable state when designing the reset circuit in Verilog, whether it is synchronous reset or asynchronous reset, there is a problem of metastable state. Here is an example of...
Understanding for synchronous release of asynchronous reset
Understanding for synchronous release of asynchronous reset Foreword First, Removal Timing Check and Recovery Timing Check definition 1.Removal Timing Check 2.Recovery Timing Check Second, the princip...
FPGA asynchronous reset synchronous release
Asynchronous reset, synchronous release: Reference synchronous reset and asynchronous reset: This figure is from the teacher's core courses. Refer to the two posts: Asynchronous reset, synchronous rel...
Asynchronous reset, synchronous release [transfer]
Asynchronous reset synchronization release circuit When performing timing analysis, it is necessary to ensure that the transmitted signal meets the establishment time and hold time, avoiding the sampl...
Availability - asynchronous reset synchronous release
There are three ways to eliminate metastasis: Synchronous processing for asynchronous signals Using FIFO to communicate across clock domain data Use asynchronous reset to the reset circuit, synchronou...
More Recommendation
Asynchronous reset and synchronous release problem
1. Asynchronous reset easily causes the output to be sub -stable (that is, unstable output) If the release time of the release of the asynchronous reset signal and the effective along the clock is alm...
Asynchronous reset synchronous release understanding
code: always @ (posedge clk, negedge rst_async_n) if (!rst_async_n) begin rst_s1 <= 1’b0; rst_s2 <= 1’b0; end else begin rst_s1 <= 1’b1; rst_s2 <= rst_s1; end This circui...
Asynchronous reset synchronous release [FPGA]
Reset is to restore the on-chip registers to the initial state, and release means that the register leaves the initial state and starts to work. Common reset methods include: asynchronous reset, synch...
Comparison of synchronous reset and asynchronous reset
Comparison of synchronous reset and asynchronous reset First, the characteristics: Synchronous reset: As the ...
VHDL synchronous reset and asynchronous reset
Article first published onMy personal blog Synchronous reset Only when the "clock edge" comes, the reset can be completed. Asynchronous reset Regardless of whether the "clock edge"...