How is a SQL query statement executed?
This article will introduce MySQL's infrastructure through a SQL execution process.
First, there is a user_info table with an id field. Execute the following query:
select * from user_info where id = 1;The return result is:
+----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------------------+---------------------+
| id | username | password | openid | role | create_time | update_time |
+----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------------------+---------------------+
1 | Wu Peixuan | 123 | 1 | 1 | 2019-08-29 00:29:08 | 2019-08-29 00:29:08 |
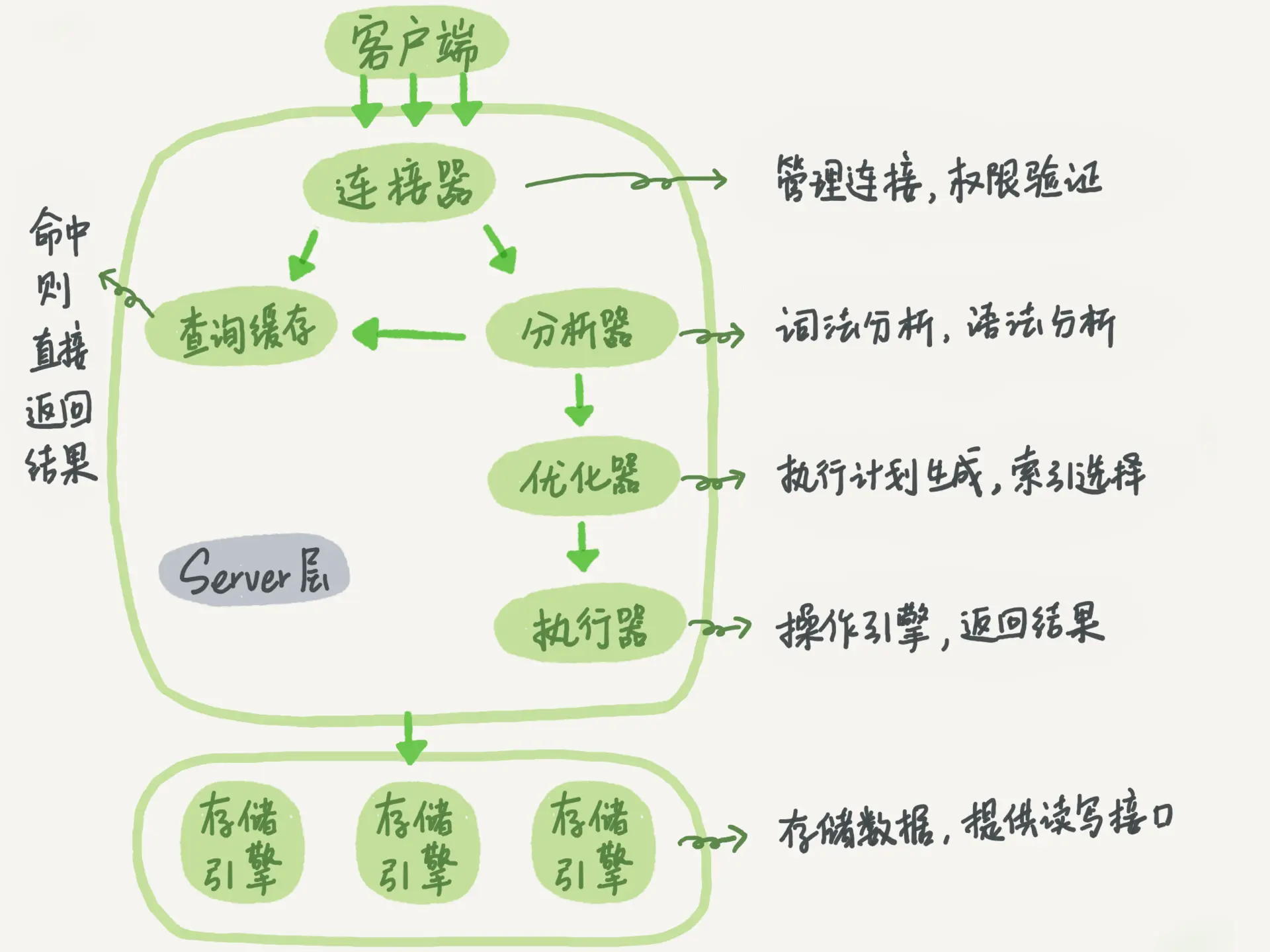
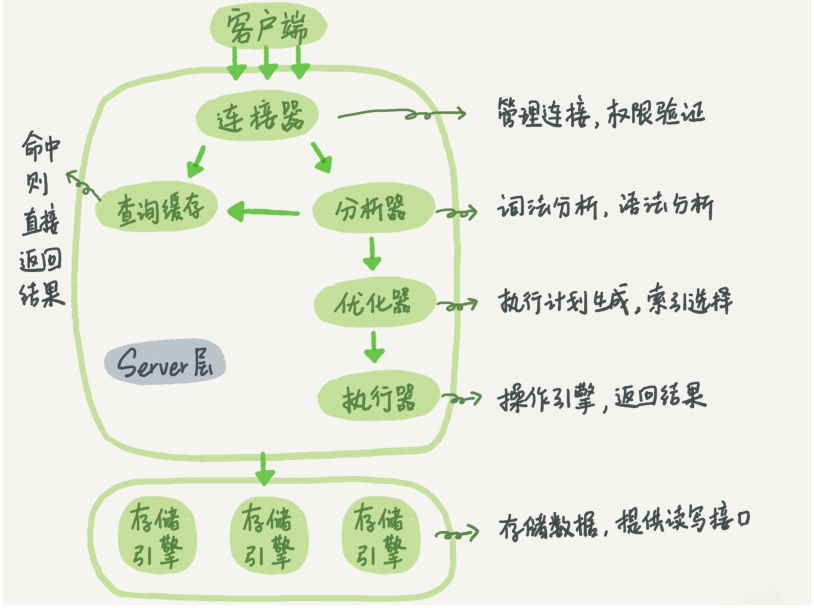
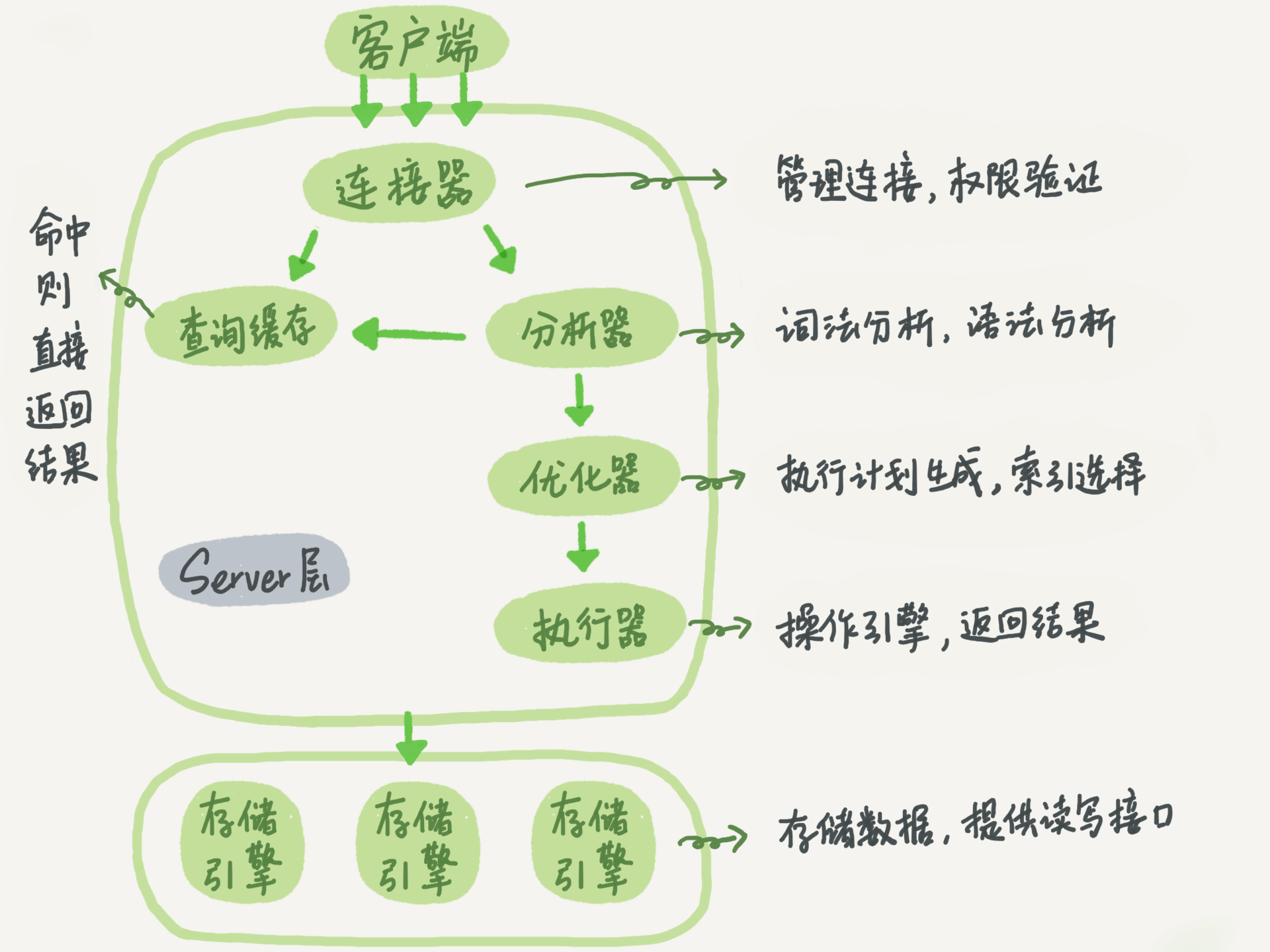
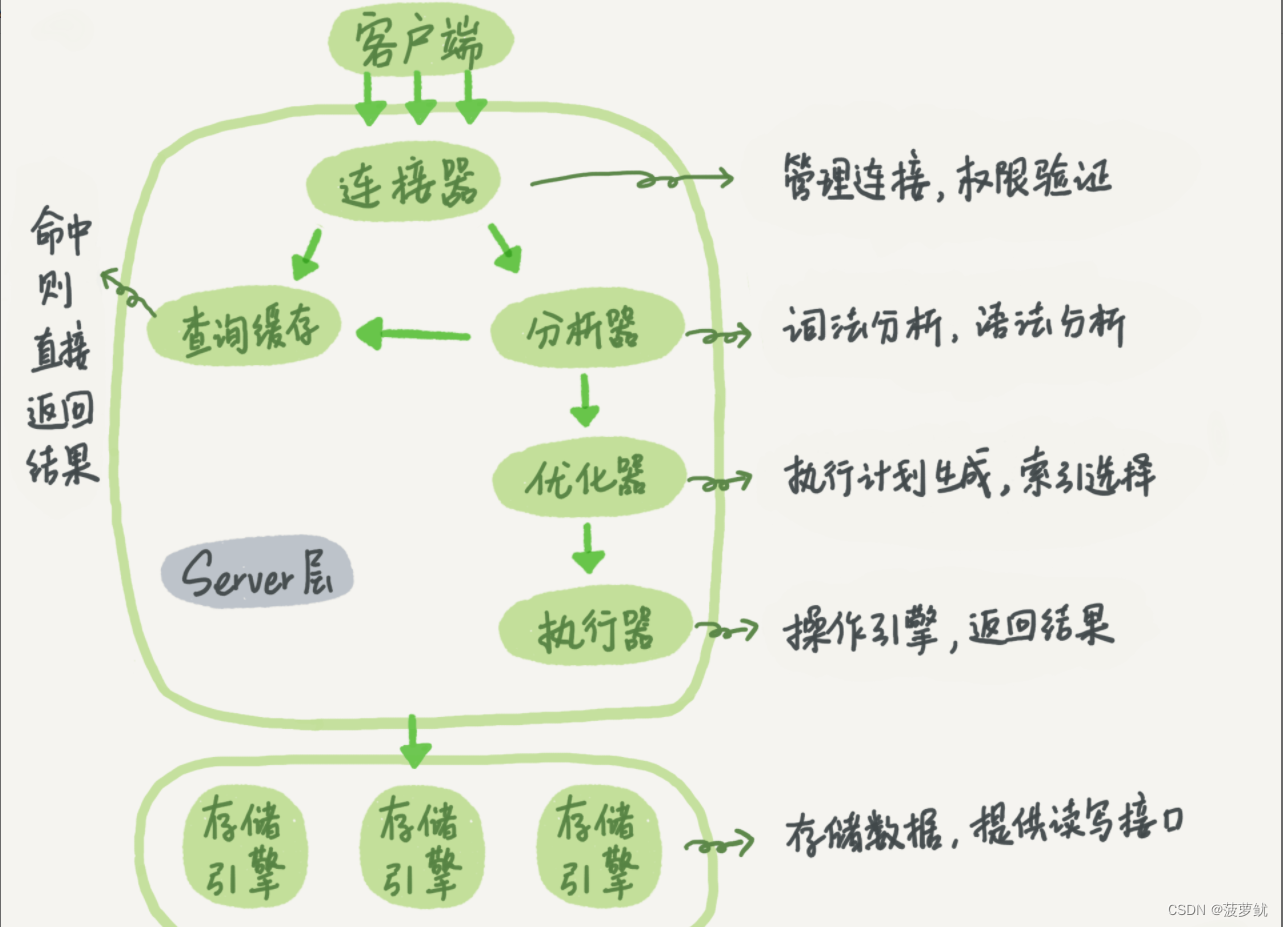
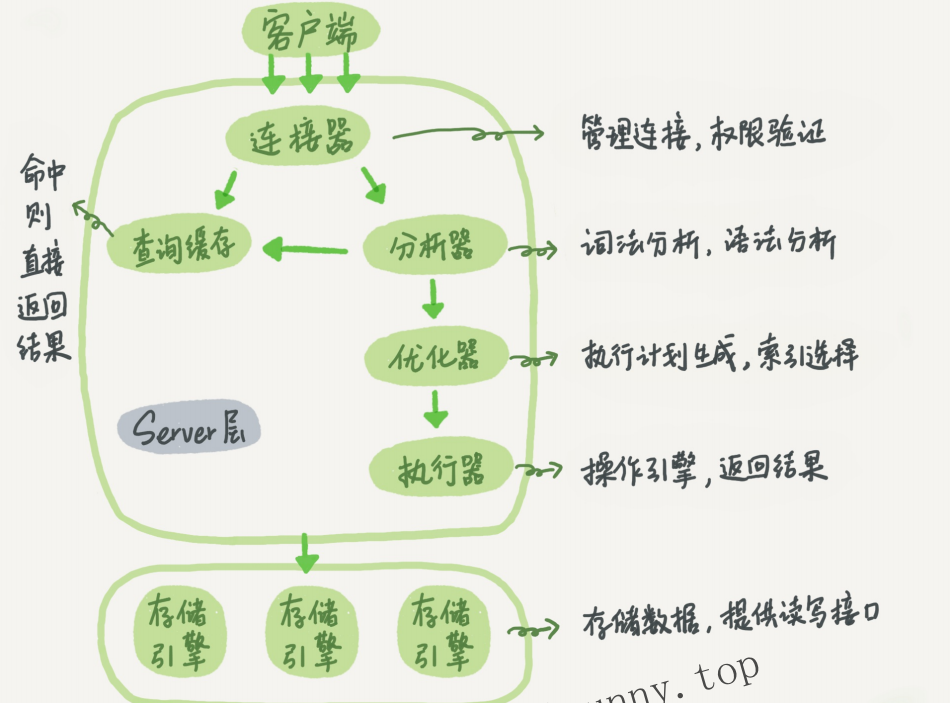
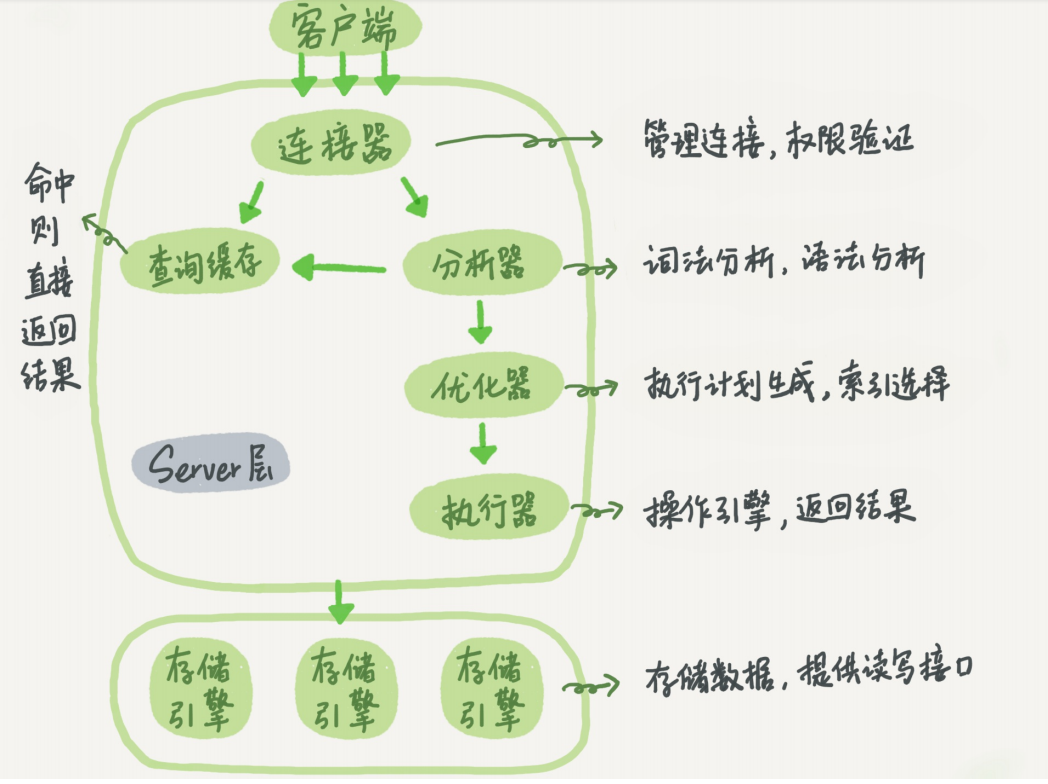
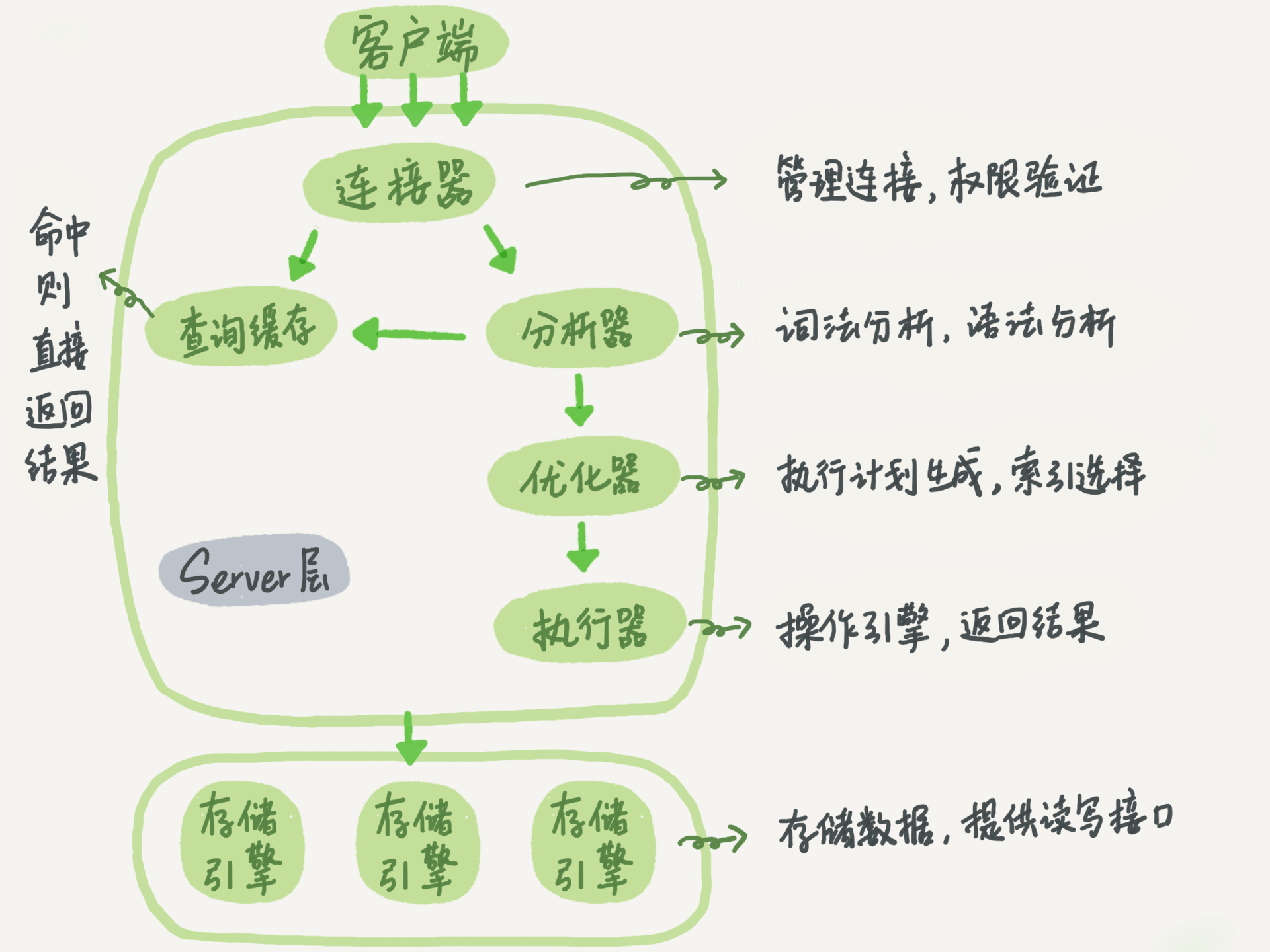
+----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------------------+---------------------+The following is a schematic diagram of the basic architecture of MySQL. You can see the execution process of SQL statements in each module of MySQL.
MySQL basic architecture
Doraemon https://wap.guxs.net/
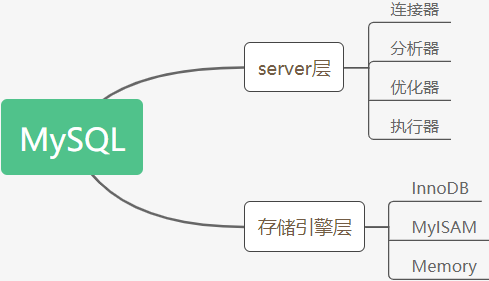
In general, MySQL is divided into two parts: the server layer and the storage engine layer.
The Server layer includes connectors, query cache, analyzers, executors, etc., as well as all built-in functions (such as date, time, math, and encryption functions) and cross-storage engine functions (such as stored procedures, triggers, and views).
The storage engine layer is responsible for data storage and retrieval, and supports multiple storage engines such as InnoDB, MyISAM, and Memory. After MySQL 5.5.5, the default storage engine is InnoDB.
Connector
Before querying SQL statements, you must first establish a connection with MySQL, which is done by the connector. The connector is responsible for establishing a connection with the client, obtaining permissions, maintaining and managing the connection. The connection command is:
mysql -h$ip -P$port -u$user -p Enter the password, after verification, the connector will go to the permissions table to find out the permissions you have, and then the permission judgment logic in this connection will depend on the permissions read at this time. After a user successfully establishes a connection, even if the management The permission of the user has been modified, and it will not affect the permission of the existing connection. After the modification, only the newly created connection will use the new permission setting.
After the connection is completed, if you have no follow-up action, the connection is idle, you canshow processlist See it in the command. The results are as follows:
+----+------+----------------+------------------+---------+------+----------+------------------+
| Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info |
+----+------+----------------+------------------+---------+------+----------+------------------+
| 3 | root | localhost:2790 | NULL | Sleep | 5878 | | NULL |
| 4 | root | localhost:2791 | springcloud_sell | Sleep | 5838 | | NULL |
| 7 | root | localhost:2900 | springcloud_sell | Sleep | 5838 | | NULL |
| 10 | root | localhost:3627 | springcloud_sell | Query | 0 | starting | show processlist |
+----+------+----------------+------------------+---------+------+----------+------------------+If the client has not moved for a long time, the connector will automatically disconnect it; this time is controlled by the parameter wait_timeout, the default value is 8 hours. If the client sends a request again after the connection is disconnected, it will receive an error reminder:Lost connection to MySQL server during query。
Long connection and short connection
- In the database, long connection means that after the connection is successful, if the client continues to request, it will always use the same connection.
- Short connection means that each time a few queries are executed, the connection is disconnected, and the next query is re-established.
The process of establishing a connection is usually more complicated. It is recommended to minimize the actions of establishing a connection and use a long connection as much as possible. However, after all long connections are used, sometimes the memory occupied by MySQL rises particularly fast. This is because the memory temporarily used by MySQL during execution is managed in the connection object. These resources will be disconnected
is only released when it is open. Therefore, if long connections accumulate, it may cause too much memory usage and be forcibly killed by the system (OOM). From the perspective of the phenomenon, MySQL has restarted abnormally.
How to solve this problem? The following two schemes can be considered:
- Disconnect long connections regularly. After using for a period of time, or after the program determines that a large query that occupies memory has been executed, disconnect the connection, and then reconnect the query.
- For MySQL 5.7 and above, you can reinitialize the connection resources by executing mysql_reset_connection after each large operation. This process does not require reconnection and permission verification, but will restore the connection to the state it was just created.
Query Cache
After the connection is established, the select statement is executed, and the cache is first queried before execution.
After MySQL gets the query request, it will first query the cache to see if this statement has been executed. The executed statement and its result will be saved in a certain memory area in the form of key-value pairs. key is the query statement, and value is the result of the query. If your query can directly find the key in this cache, then this
value will be returned directly to the client.
If the statement is not in the query cache, it will continue to the next stage of execution. After the execution is completed, the execution result will be stored in the query cache. If the query hits the cache, MySQL can directly return the result without performing complicated operations later, which will improve efficiency.
However, the query cache is very invalid. As long as there is an update to a table, all query caches on this table will be cleared. For databases under heavy pressure, the hit rate of the query cache will be very low. If a static table is needed in the business, it will only be updated once in a long time. For example, a system configuration table, then the query on this table is suitable for using query cache. MySQL provides this on-demand approach. You can set the parameter query_cache_type to DEMAND, and query cache will not be used for the default SQL statements. And for the statement you are sure to use query cache, you can use SQL_CACHE to specify explicitly, as follows:
mysql> select SQL_CACHE * from user_info where id = 1;MySQL 8.0 version removes the query cache function.
Analyzer
If the query cache misses, it is time to execute the statement. First, MySQL needs to parse SQL statements.
The analyzer will do lexical analysis first. The SQL statement is composed of multiple strings and spaces. MySQL needs to recognize what the strings are and what they represent. MySQL recognizes this keyword from the select keyword you entered, which is a query statement. It also recognizes the string user_info as the table name and the string id as the column name. After that, we need to do grammatical analysis. According to the result of lexical analysis, the grammar analyzer will determine whether the input SQL statement meets the MySQL grammar according to the grammar rules.
If your SQL statement is wrong, you will receiveYou have an error in your SQL syntax Error reminders, such as the following statement from written into form.
mysql> select * form user_info where id = 1;
1064 - You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'form user_info where id = 1' at line 1General grammatical errors will prompt the first place where the error occurred, so the immediate concern isuse near Content.
Optimizer
After the lexical analysis and grammatical analysis of the analyzer, it is also processed by the optimizer.
The optimizer decides which index to use when there are multiple indexes in the table; or when a statement has multiple table joins (join), decides the connection order of each table. For example, if you execute the following statement, this statement is to perform a join of two tables:
mysql> SELECT * FROM order_master JOIN order_detail USING (order_id) WHERE order_master.pay_status = 0 AND order_detail.detail_id = 1558963262141624521;You can first take the order_id value of the record with pay_status = 0 from the table order_master, and then associate it with the order_detail table according to the order_id value, and then determine whether the value of detail_id in order_detail is equal to 1558963262141624521.
You can also take the order_id value of the record with detail_id = 1558963262141624521 from the order_detail table, and then associate it with the order_master according to the order_id value, and then determine whether the value of pay_status in order_master is equal to 0.
The logical results of these two execution methods are the same, but the efficiency of execution will be different, and the role of the optimizer is to decide which program to use. After the optimizer phase is completed, the execution plan of this statement is determined, and then enter the executor phase.
Actuator
MySQL knows what to do through the analyzer, and knows what to do through the optimizer, so it enters the executor stage and starts executing statements.
When starting execution, first determine whether you have permission to execute a query on this table user_info. If not, it will return an error without permission, as shown below (if you hit the query cache, when the query cache returns the result, Do permissions verification. The query will also call precheck to verify permissions before the optimizer).
mysql> select * from user_info where id = 1;
ERROR 1142 (42000): SELECT command denied to user 'wupx'@'localhost' for table 'user_info'If you have permission, open the table to continue execution. When the table is opened, the executor will use the interface provided by the engine according to the table's engine definition. For example, in the table user_info in our example, the id field has no index, so the execution flow of the executor is as follows:
- Call the InnoDB engine interface to fetch the first row of this table, determine if the id value is 1, if not, skip it, and if so, store this row in the result set;
- Call the engine interface to fetch the next row and repeat the same judgment logic until the last row of this table is fetched.
- The executor returns a record set composed of all the rows that satisfy the condition in the above traversal process as a result set to the client.
For an indexed table, the first call is to take the interface that meets the first row of the condition, and then fetch the interface that meets the condition for the next row in a loop.
There is a rows_examined field in the slow query log of the database, indicating how many rows were scanned during the execution of this statement. This value is accumulated every time the executor calls the engine to get the data row. In some scenarios, the executor is called once, and multiple lines are scanned inside the engine, so the number of lines scanned by the engine is not exactly the same as rows_examined.
to sum up
Mainly by explaining the complete execution process of a SQL statement, the logical structure of MySQL is introduced. MySQL mainly includes several modules: connector, query cache, analyzer, optimizer, and executor.
Intelligent Recommendation
How is a SQL query statement executed? MySQL talks
In the world, the beautiful application experience is from the programmer to the details of the details and the realm of self-demanding, the young people are also a busy code farmers, every day, weekl...
How is the mysql SQL query statement is executed
The next article about the mysql infrastructure is from the mysql actual combat 45 for the polar time. MySQL is actually a short written by My Ess Que Ell Mysql's infrastructure schematic: Greatly, My...
MySQL01 - How is a SQL query statement executed?
This note is I learned the Terminal Time Course - Mysql45 taking note, if there is infringement, please contact, remove! 1 How is the SQL query statement executed? The SQL statement discussed in this ...
01 | Infrastructure: How is a SQL query statement executed?
Article catalog Basic architecture of mysql Server layer Storage engine layer Connector Question: Using long connection memory rises so fast? Problem: Long connection causes mysql abnormal restart Que...
01. Infrastructure: How is a SQL query statement executed?
Article catalog 1. MySQL architecture 2. Connector 3. Query cache 4. Analyzer 5. Optimizer 6. Actuator problem 1. Long connection, short connection meaning 2. All long connections can cause Mysql memo...
More Recommendation
01 Infrastructure: How is a SQL query statement executed
In front No matter what is doing in life, or learning a new technology, you must notPipe peeping leopard Instead, it is necessary to look at the overall situation, because only by controlling the over...
Day1: How is a SQL query statement executed
The most commonly used inquiries of MySQL database are the query function, but after a query statement is sent from the client to the server, all we see is that the database returns a result. MySQL ar...
MySQL: How is a SQL query statement executed?
1. MySQL's logical architecture diagram MySQL is divided into two parts: Server layer and storage engine layer. The Server layer includes: connectors, query cache, analyzer, optimizer, actuator, etc.,...
Infrastructure: How is a SQL query statement executed?
What we see is to enter a statement and return a result, but we don't know the execution process of this statement in the internal Mysql. The basic architecture of MySQL Generally speaking, mysql can ...
mysql-1. How is a SQL query statement executed?
mysql mysql45 lecture notes A simple SQL statement query MySQL logical architecture MySQL can be divided into two parts: Server layer and storage engine layer. server layer The Server layer includes c...