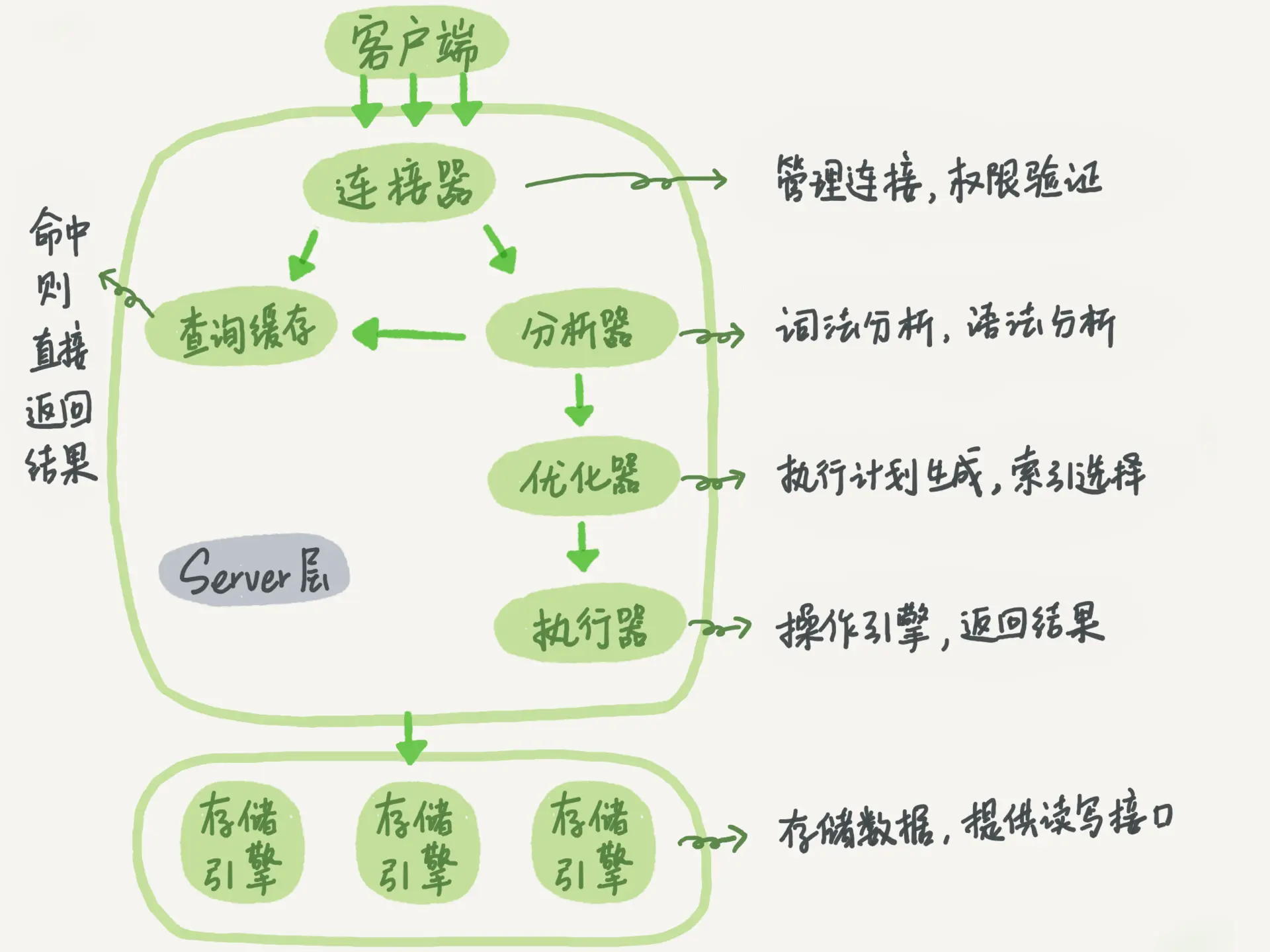
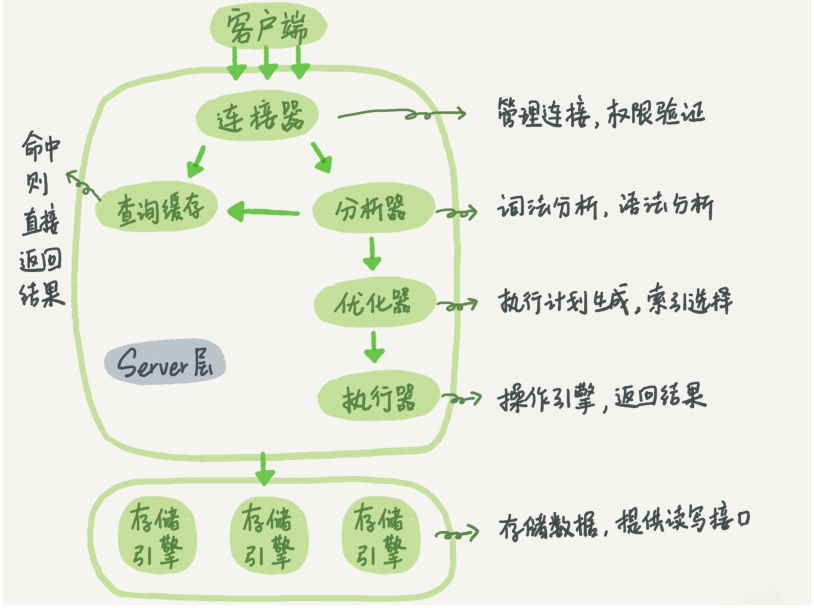
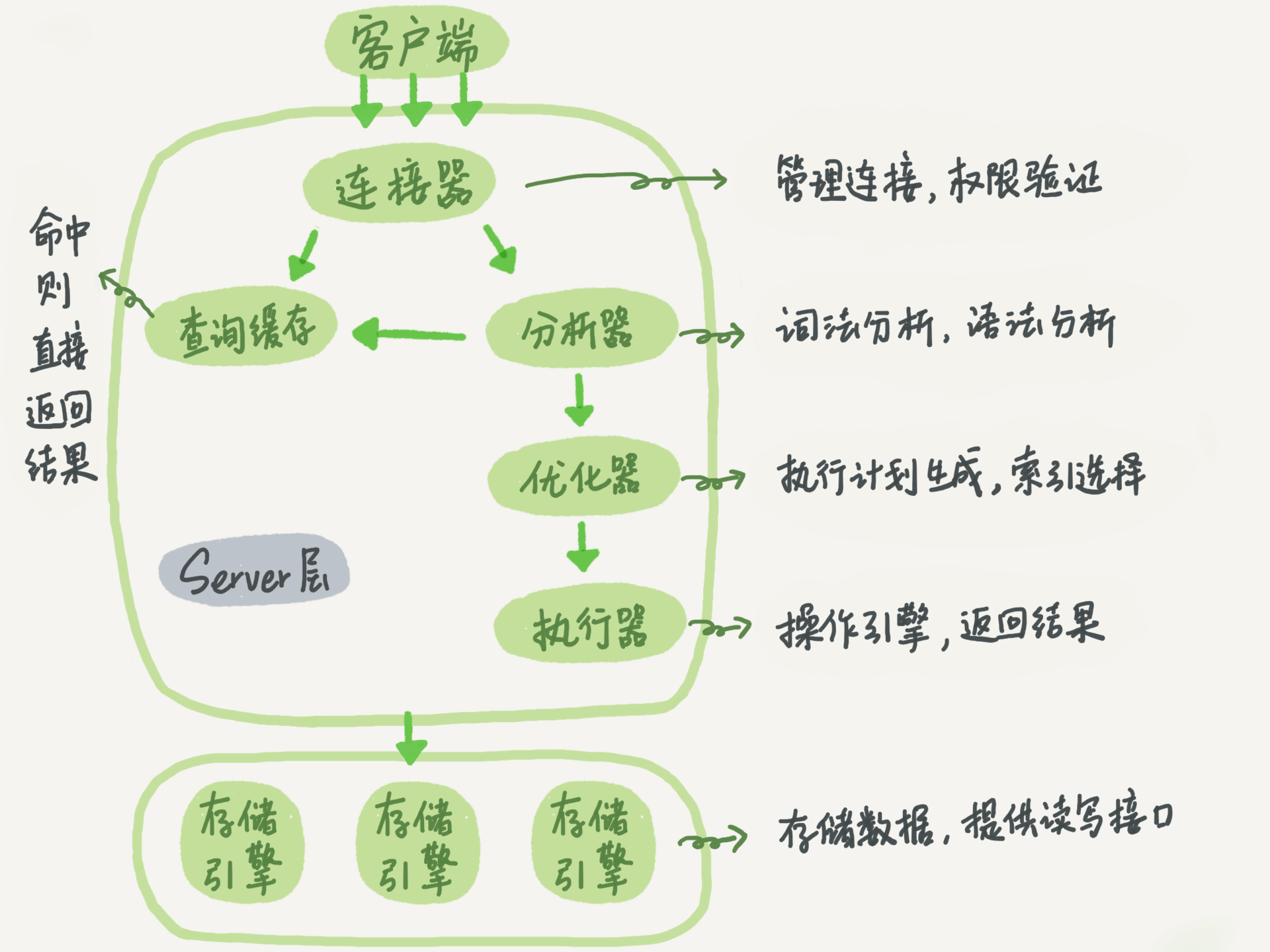
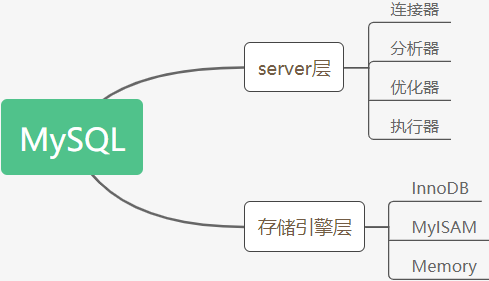
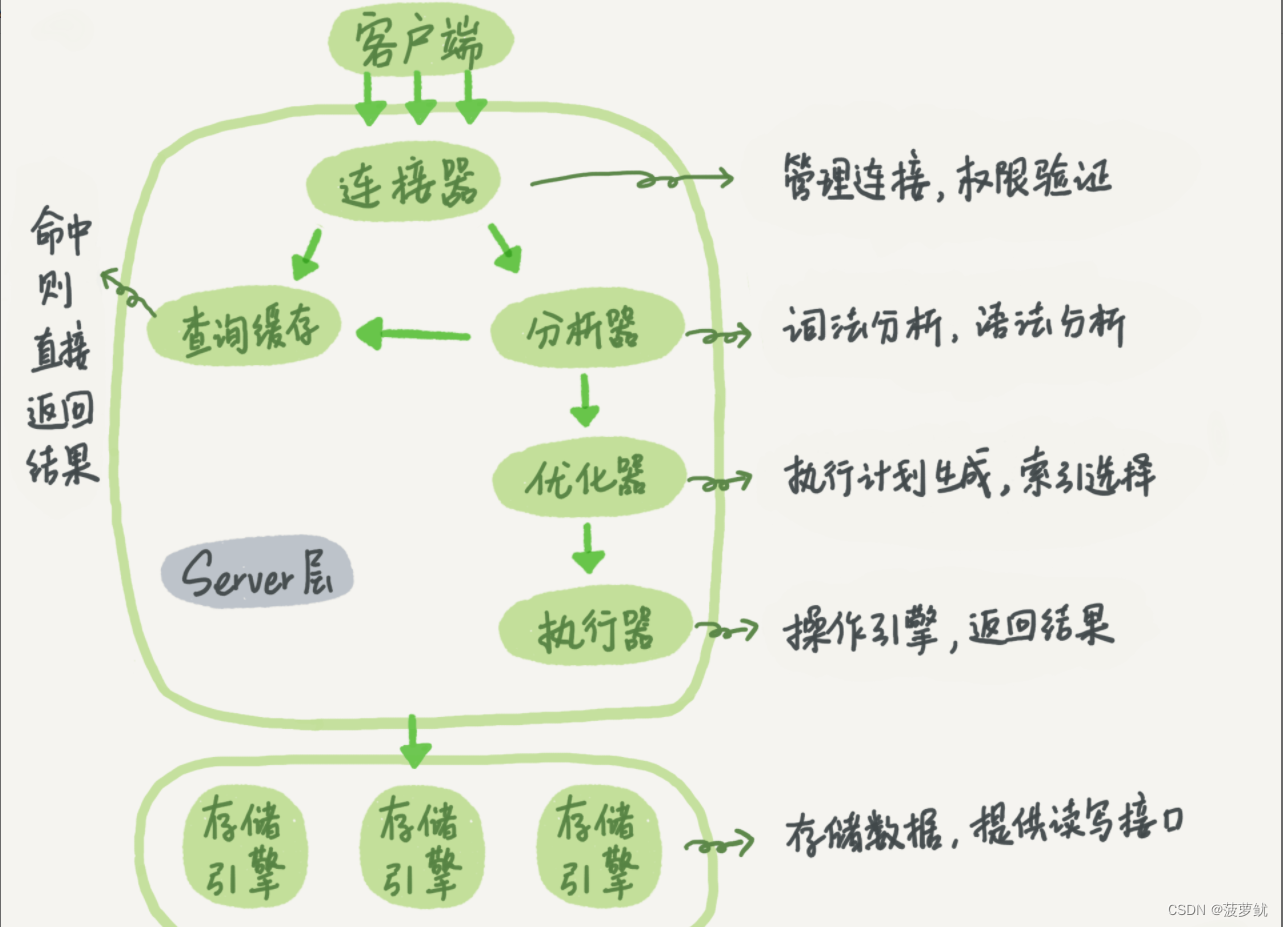
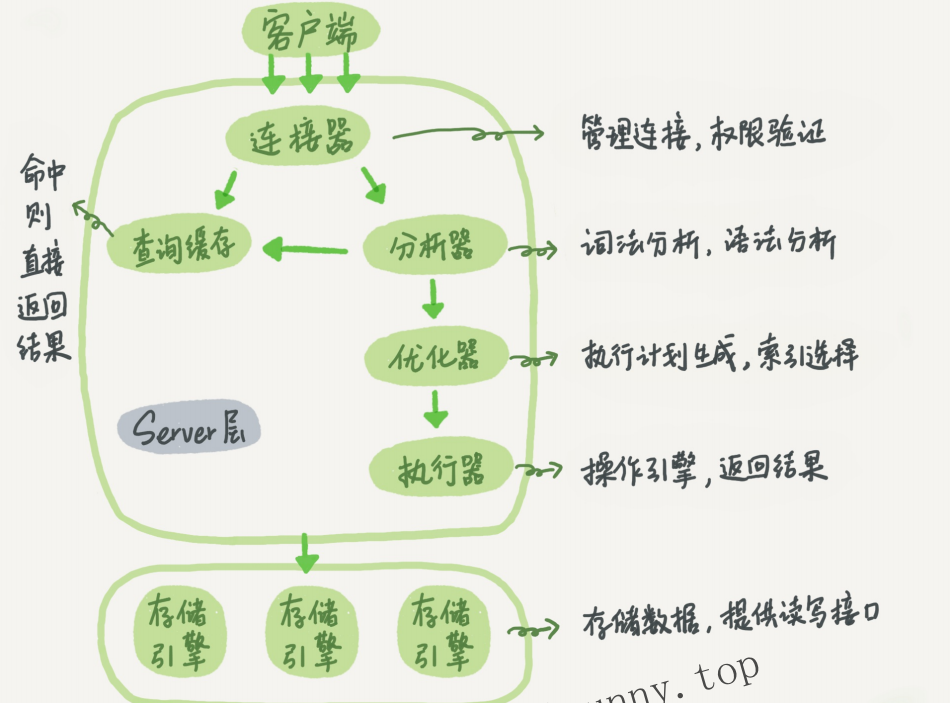
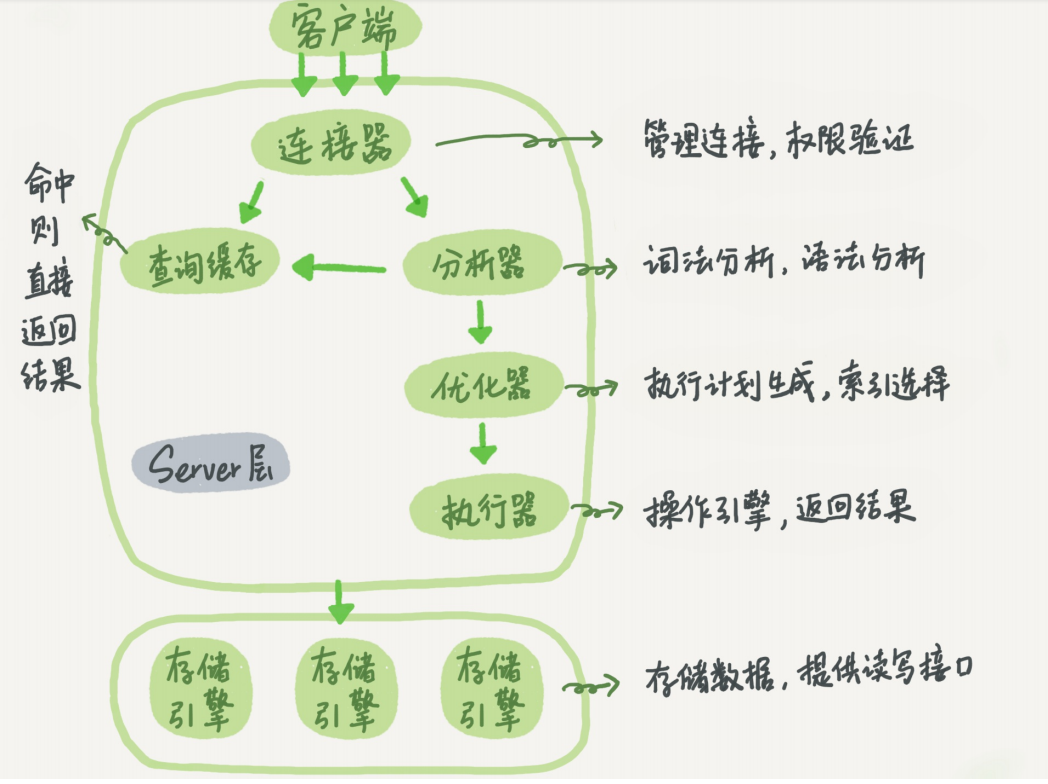
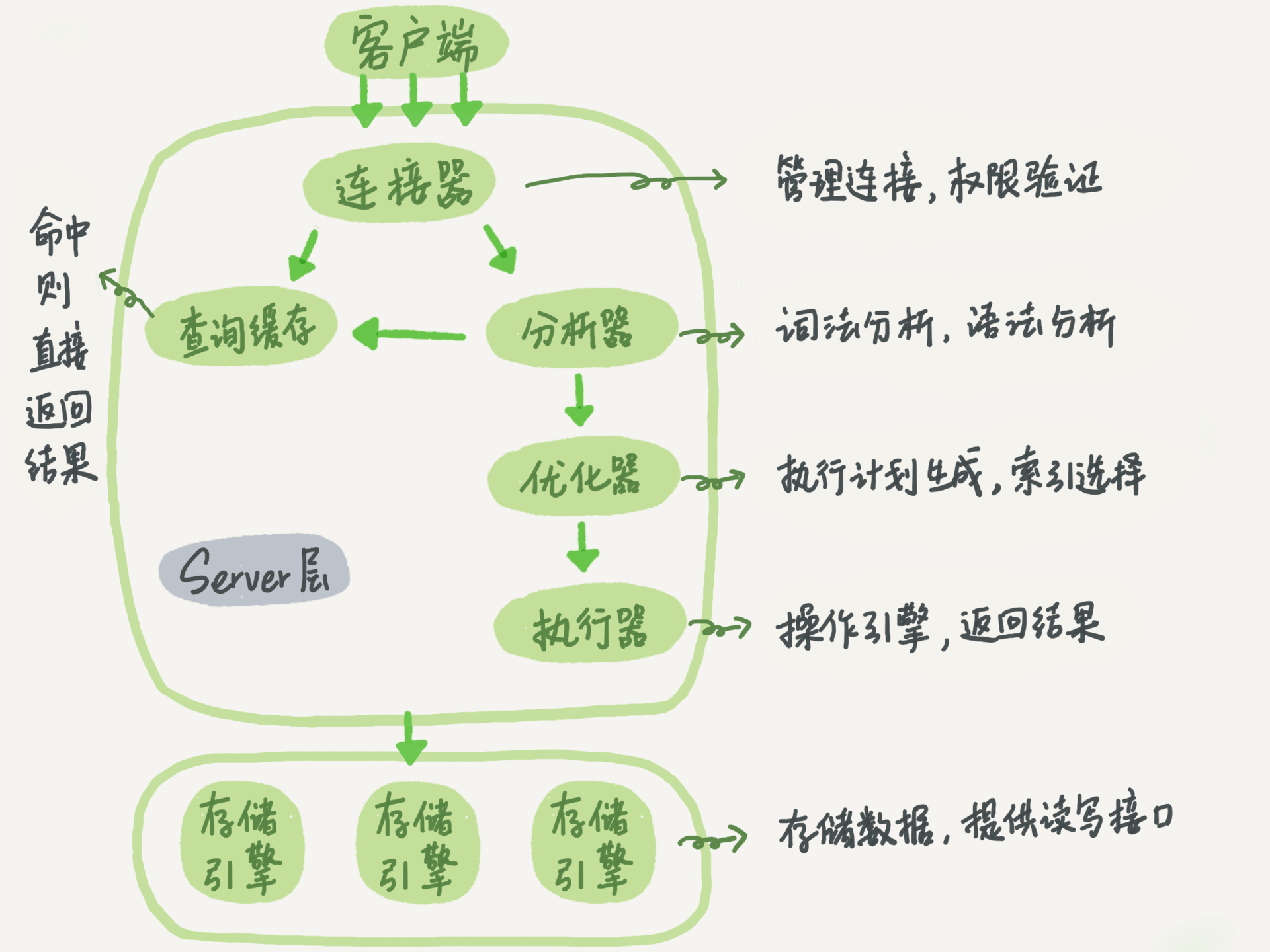
Connector
In the first step, you will first connect to this database. At this time, you will receive the connector. The connector is responsible for establishing a connection with the client, obtaining permissions, maintaining and managing the connection. The connection command is generally written like this:
mysql -h$ip -P$port -u$user -p
After entering the command, you need to enter the password in the interactive dialog. Although the password can also be written directly on the command line after -p, this may cause your password to be revealed. If you are connected to a production server, it is strongly recommended that you do not do this. Mysql in the connection command is a client tool used to establish a connection with the server. After completing the classic TCP handshake, the connector will begin to authenticate your identity. At this time, the user name and password you entered are used.
If the user name or password is incorrect, you will receive an "Access denied for user" error, and then the client program ends. If the username and password are authenticated, the connector will go to the permissions table to find out the permissions you have. After that, the logic for determining the authority in this connection will depend on the authority read at this time. This means that after a user successfully establishes a connection, even if you modify the user's permissions with an administrator account, it will not affect the permissions of the existing connection. After the modification is completed, only the newly created connection will use the new permissionsAfter the connection is completed, if you have no follow-up action, the connection is idle, you can show in
See it in the processlist command. The figure in the text is the result of show processlist. The Command column shows the line "Sleep", which means that there is an idle connection in the system. If the client has not moved for a long time, the connector will automatically disconnect it. This time is determined by the parameter wait_timeout
Controlled, the default value is 8 hours.
If the client sends a request again after the connection is disconnected, you will receive an error reminder: Lost connection to MySQL server during query. At this time, if you want to continue, you need to reconnect, and then execute the request. In the database, long connection means that after the connection is successful, if the client continues to request, it will always use the same connection. Short connection means that each time a few queries are executed, the connection is disconnected, and the next query is re-established. The process of establishing a connection is usually more complicated, so I suggest you to minimize the action of establishing a connection, that is, use a long connection as much as possible. However, after using all long connections, you may find that sometimes the memory occupied by MySQL rises particularly fast. This is because the memory temporarily used by MySQL during execution is managed in the connection object. These resources will only be released when the connection is broken. Therefore, if long connections accumulate, it may cause too much memory usage and be forcibly killed by the system (OOM). From the perspective of the phenomenon, MySQL has restarted abnormally.
How to solve this problem? You can consider the following two options.
1. Regularly disconnect long connections. After using for a period of time, or after the program determines that a large query that occupies memory has been executed, the connection is disconnected, and then the query must be reconnected.
2. If you are using MySQL 5.7 or later, you can reinitialize the connection resources by executing mysql_reset_connection after each time you perform a relatively large operation. This process does not require reconnection and re-authorization, but will restore the connection to the state it was just created.
Query cache
After the connection is established, you can execute the select statement. The execution logic will come to the second step: query cache. After MySQL gets a query request, it will first go to the query cache to see if this statement has been executed before. The previously executed statements and their results may be directly cached in memory in the form of key-value pairs. key is the query statement, and value is the result of the query. If your query can find the key directly in the cache, then this value will be returned directly to the client.
If the statement is not in the query cache, it will continue to the subsequent execution stage. After the execution is completed, the execution result will be stored in the query cache. As you can see, if the query hits the cache, MySQL can directly return the result without performing complicated operations later, which is very efficient.
But in most cases, I would advise you not to use query caching, why? Because query cache is often more harmful than
Profit.
The query cache is very invalid. As long as there is an update to a table, all query caches on this table will be cleared. Therefore, it is very likely that you will have to save the result with great effort, and it will be completely cleared by an update before it is used. For databases under heavy pressure to update, the query cache hit rate will be very low. Unless your business is to have a static table, it will only be updated once in a long time. For example, a system configuration table, then the query on this table is suitable for using query cache. Fortunately, MySQL also provides this "on-demand" approach. You can set the parameter query_cache_type to DEMAND, so that query cache is not used for the default SQL statements. For the statement you are sure to use the query cache, you can use SQL_CACHE to specify it explicitly, like the following statement:
Copy code
mysql> select SQL_CACHE * from T where ID=10;
It should be noted that the MySQL 8.0 version directly deletes the entire function of the query cache, which means that this function has not been available since 8.0.
Analyzer