Repayment of debts, Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2) -D (multiple backpacks)
tags: Backpack dp algorithm Dynamic programming
Description
llk and wy often go to the yh restaurant to have rice with toppings. One day after they finished eating, llk paid the two people's money together, but wy did not want to owe llk the money. Now wy has some loose money in his hands, and llk also has some loose money in his hands. wy wants to know if they can just make the two owe each other, but wy is stupid, can you help wy?
Input
For multiple groups of test data, enter 3 non-negative integers, C, n, m in the first line of each group. C represents the money wy owes llk, n represents the type of face value of the money in wy, and m represents the type of face value of the money in llk. In the next n lines, each line contains two numbers v and c, which respectively represent c coins with face value v in wy's hand. In the next m rows, there are two numbers v and c in each row, representing c coins with face value v in llk's hand. (C <= 10000; 1<=n, m<50; 0<=v <=100; 0<=c<=10)
Output
Each group of data outputs one line. If there is a scheme to make wy and llk not owe, output YES, otherwise output NO.
Sample Input
7 1 1
10 1
1 10
Idea: Multiple backpacks record the existence of dp. Let p[] be the money that wy may collect, q[] is the money that llk may collect, dp respectively, and find whether there is p[i]==q[i-c]==1.
dp status: dp[i] means whether the amount of money i can be collected
dp transfer: dp[j] |= dp[j-k*v[i]
#include <math.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#define ll long long
#define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e5+5;
struct node{
int v,c;
};
node a[55],b[55];
int p[50050];
int q[50050];
int main()
{
int c,n,m;
while(cin>>c>>n>>m){
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
memset(q,0,sizeof(q));
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i].v>>a[i].c;
sum+=a[i].v*a[i].c;
}
p[0]=q[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=a[i].c;j++){
for(int k=a[i].v*j;k<=sum;k++){
p[k]|=p[k-a[i].v*j];
}
}
}
sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cin>>b[i].v>>b[i].c;
sum+=b[i].v*b[i].c;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=b[i].c;j++){
for(int k=b[i].v*j;k<=sum;k++){
q[k]|=q[k-b[i].v*j];
}
}
}
int flag=0;
for(int i=c;i<=50000;i++){
if(p[i]==1&&q[i-c]==1){
flag=1;break;
}
}
if(flag) printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
}
Then there is a similar question that can be done with backpack + greedy.
Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2) -D
The meaning of the question is probably that some pieces of the LED segment are broken, and you can only and must fix k pieces of it, no more, no less. Ask what is the maximum number that can be displayed after repairing.
 Idea: It can also be transformed into a problem of backpack existence. For each LED, we judge the number that can be modified. For example, 0->8 consumes 1, 1->7 consumes 1. Of course, some cases cannot be modified, such as 1->5. After the LED is calculated, it can be transformed into a backpack problem:
Idea: It can also be transformed into a problem of backpack existence. For each LED, we judge the number that can be modified. For example, 0->8 consumes 1, 1->7 consumes 1. Of course, some cases cannot be modified, such as 1->5. After the LED is calculated, it can be transformed into a backpack problem:
dp from back to front to see if dp[0] [0] == 1. If it is 0, there must be no such backpack, and -1 is output. If it does exist, look at the case of compliance from the front to the back from the 9-0 priority. So in essence, it is similar to optimizing the path of the backpack.
Why not from front to back dp: Our final greedy method is to take from front to back, and the dp from back to front is the path of the backpack (proving that the current point can definitely reach the end point )
dp state: dp [i] [j] refers to whether the i-th segment exists, and it costs j
dp transfer: dp[i] [j-cnt] |= dp[i+1] [j];
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#define ll long long
#define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e3+5;
int n,k;
string t[10]={
"1110111", "0010010", "1011101", "1011011", "0111010", "1101011", "1101111", "1010010", "1111111", "1111011"
};
string s[maxn];
struct node{
int cost,v;
};
vector<node>g[maxn];
int dp[maxn][maxn];
int main()
{
cin>>n>>k;
//for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>s[i];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>s[i];
for(int j=9;j>=0;j--){
int cnt=0,flag=1;
for(int k=0;k<7;k++){
if(s[i][k]=='1'&&t[j][k]=='0'){
flag=0;break;
}
cnt+=(s[i][k]=='0'&&t[j][k]=='1');
}
if(flag) g[i].push_back({cnt,j});
}
}
//The initial value is set to 1
dp[n][k]=1;
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=0;j<g[i].size();j++){
int cnt=g[i][j].cost,val=g[i][j].v;
for(int p=cnt;p<=k;p++){
dp[i][p-cnt]|=dp[i+1][p];
}
}
}
if(!dp[0][0]){
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
int cnt=0;
//Greedy-take the best solution from 9-0
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<g[i].size();j++){
if(cnt+g[i][j].cost>k) continue;
if(dp[i+1][cnt+g[i][j].cost]){
printf("%d",g[i][j].v);
cnt+=g[i][j].cost;
break;
}
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Intelligent Recommendation
Solution-Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2,A-E)
C o d e f o r c e s R o u n d 637 ( D i v . 2 A − E ) \mathrm{Codeforces\ Round \ 637 \ (Div. 2\ A-E) } Codeforces Round 637 (Div.2 A−E) A ....
D. Nastya and Scoreboard (dp || dfs)Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2) - Thanks, Ivan Belonogov!
Title: There are n 7-digit digital digital cards (some are missing in the middle), given k sticks as a supplement, ask what is the largest number that can be formed Ideas: d p [ i ] [ j ] dp[i][j] dp[...
Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2)-Thanks, Ivan Belonogov! D. Nastya and Scoreboard (greedy+dp)
D. Nastya and Scoreboard time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standard output Denis, who managed to buy flowers and sweets (you will learn about...
Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2)-Thanks, Ivan Belonogov! D. Nastya and Scoreboard solution (memoized search)
Topic link Topic A score board with n digital digits, each digital digit is a seven-segment digital tube, now the display status of each digital digit is given, and asked what is the largest number th...
CodeForces Round # 637 (DIV. 2) (D, Nastya and Scoreboard DP, DFS) (Training)
D - Nastya and Scoreboard The meaning:Give you the character string of the N-string from 0 and 1, the n string represents a N-bit, and one of the nth positions of each string is shown that the m...
More Recommendation
CodeCraft-19 and Codeforces Round # 537 (Div. 2) D. Destroy the Colony (dp 01 Backpack (back Backpacks))
D. Destroy the Colony Meaning of the questions: First, given a string of length n s (2 <= n <= 1e5 and n is an even number, s only lowercase letters), a good definition of the string on the left...
CodeForces Round # 428 (Div. 2): d. Winter is here (Multiple Formula)
D. Winter is here time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standard output Winter is here at the North and the White Walkers are close. John Snow h...
CodeForces Round # 717 (Div. 2) -d. CUT- (multiple)
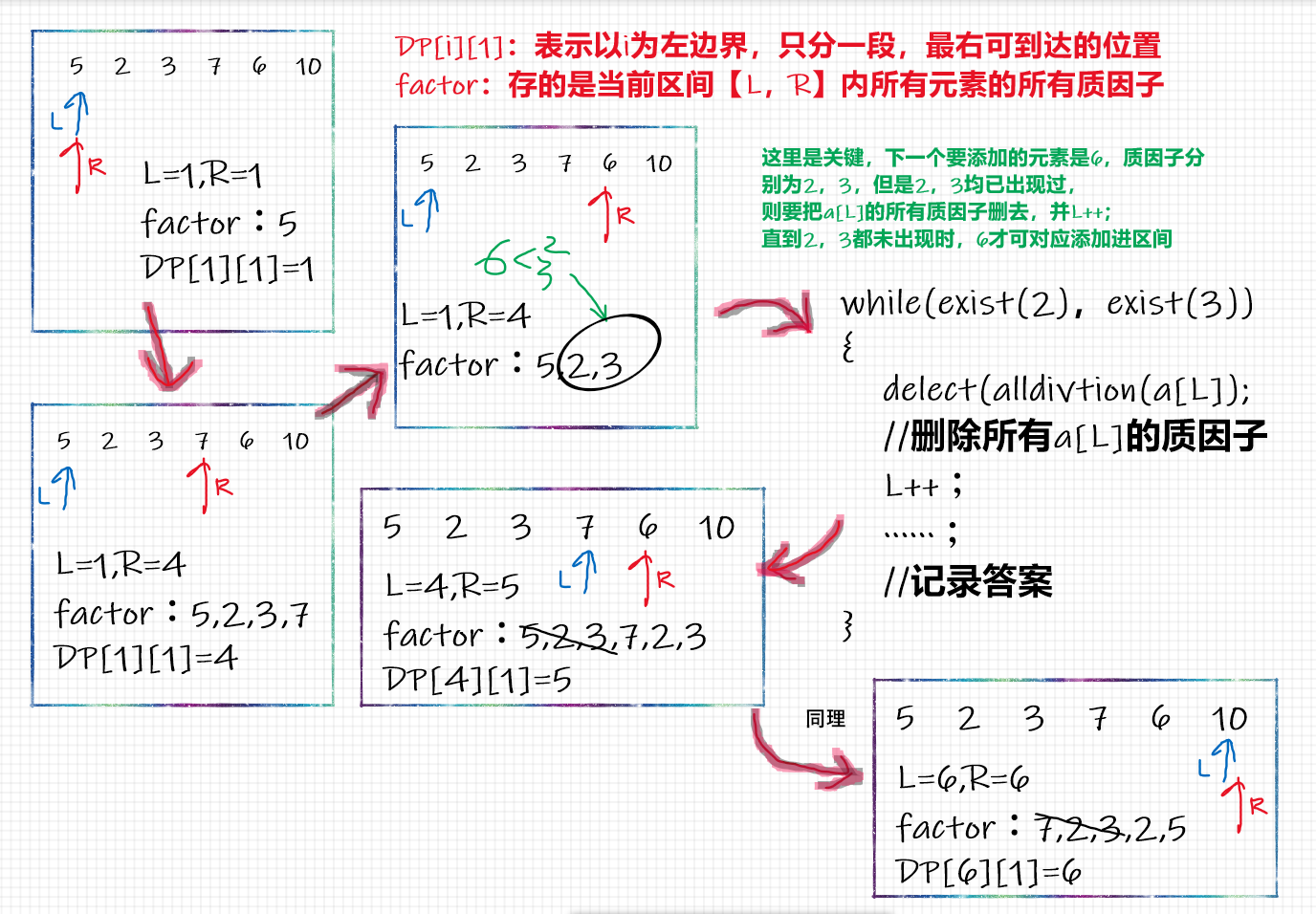
D. Cut Double pointer dynamic plan Analysis of the question can be known that all elements are all inclined, namely: GCD (A [L] ~ A [R]) = 1. First consider how to split, start from the violent method...
Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2)-A. Nastya and Rice solution
Topic link:https://codeforces.com/contest/1341/problem/A Sign-in questions, just derive from Note. code show as below:...
Codeforces Round #637 (Div. 2) ——C. Nastya and Strange Generator solution
Topic link:https://codeforces.com/contest/1341/problem/C This is a thinking question that you have to think about for a long time after you understand the question. (1) Given n, arrange the n numbers ...