Nine Backpacks: Multiple Backpacks Problem I
tags: Nine Lectures on Backpack algorithm Dynamic programming c++
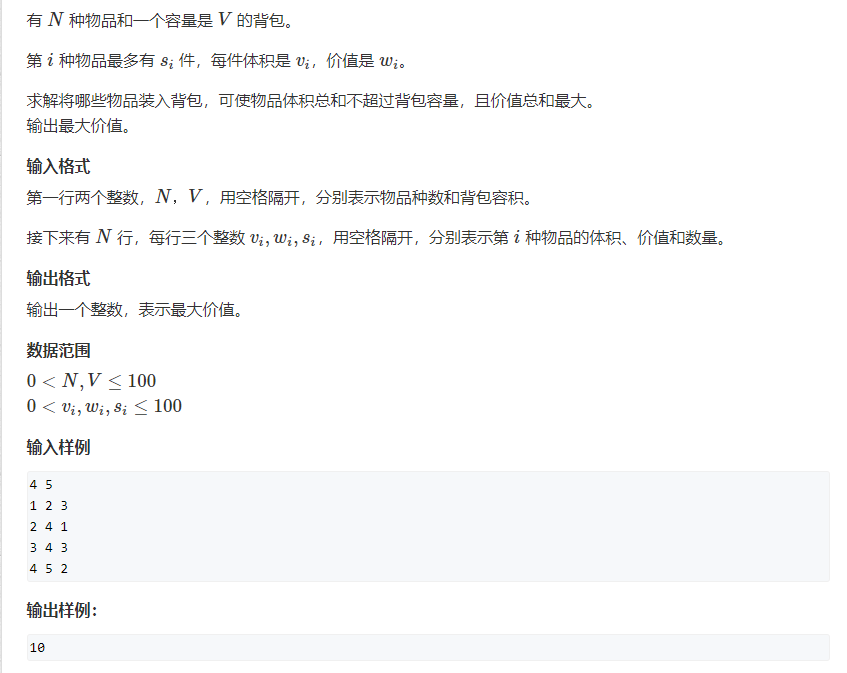
There are N items and a backpack with a capacity of V.
The i-th item has at most si Pieces, the volume of each piece is vi, The value is wi。
Solve which items are loaded into the backpack, so that the total volume of the items does not exceed the capacity of the backpack, and the total value is the largest.
Output the maximum value.
Input format
The two integers in the first line, N and V, are separated by a space, indicating the number of objects and the volume of the backpack respectively.
Next, there are N rows, each with three integers vi,wi,si, Separated by spaces, respectively indicate the volume, value and quantity of the i-th item.
Output format
outputs an integer that represents the maximum value.
data range
0<N,V≤100
0<vi,wi,si≤100
Input sample
4 5
1 2 3
2 4 1
3 4 3
4 5 2
Sample output:
10
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fun[105][105];//fun[i][j] means that only the ith item can be selected from the previous i items, and the maximum value of the volume less than or equal to j
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){// loop n items
int v,w,s;
cin>>v>>w>>s;//Enter item volume, value, quantity
for(int j=m;j>=0;j--){//Loop volume, here cannot be j>=v, because if a two-dimensional array is stored, even if it is not selected, fun[i][j]=fun[i-1][j]
for(int k=0;k<=s&&k*v<=j;k++){//Here when k=0 is to update fun[i][j]=fun[i-1][j] means that the i-th item is not selected
fun[i][j]=max(fun[i][j],fun[i-1][j-k*v]+k*w);//Select k items i
}
}
}
cout<<fun[n][m]<<endl;
return 0;
}
Binary optimized version
Intelligent Recommendation
Nine backpacks
introduction Learn about the solution to dynamic planning problems by learning the backpack and talking about this document. 1 backpack problem There are N items and a backpack with a capacity of V. T...
I love sneakers! (Multiple backpacks)
Problem Description After months of hard working, Iserlohn finally wins awesome amount of scholarship. As a great zealot of sneakers, he decides to spend all his money on them in a sneaker store. Ther...
Nine talks about headaches in backpacks (5) the problem of mixed backpacks
WeChat public account:Jerry's algorithm and NLP The knapsack problem is a classic dynamic programming model. It is simple and easy to understand, and to a certain extent can reveal the ess...
Backpack problem 3 (multiple backpacks)
The complete backpack mentioned in the previous article refers to the selection of the most value in the case of an unlimited number of items. Now the multi-clip problem is introduced, that is, the nu...
Minimum coins problem (multiple backpacks)
Time Limit: 1000 ms Memory Limit: 65536 KiB Submit Statistic Problem Description There are n coins with different denominations, and the denomination of each coin is stored in the array T[1:n]. Now I ...
More Recommendation
hdu5445 Food Problem (multiple backpacks) (*)
Topic link Food Problem Time Limit: 3000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 1731 Accepted Submission(s): 544 Problem Description Few days before a g...
[Knapsack problem] Multiple backpacks and their optimization
Article Directory Multipack I Title description Plain version code (time complexity: O(NVS)) Update while reading Use rolling array to optimize one dimension Multiple knapsack problem II (binary optim...
Backpack problem - 4. Multiple backpacks
Multiple backpack issues Topic description There are N items and a capacity of a backpack. Item I ItemUp to SIEach volume is VI, the value is Wi. Solving which items will be loaded into a backpack, wh...
[Algorithm] Backpack Problem - Multiple Backpacks
Multiple backpack Problem Description The problem of multiple backpacks is from the problem of 0-1 backpacks, and we will first understand the 0-1 backpack problem before solving multiple backpack pro...
(multiple backpacks)
Multiple knapsack problem: The number of items w[ i ] is limited and not necessarily the same, and each item has its value v[ i ], seeking the highest value in such cases. Full backpack: choose...